The purpose of this Cyber Hygiene course is to prepare a cadre of Cyber Hygiene professionals who can assist organisations to create a safer digital environment for their operations and activities.
Essential Cyber Hygiene Tips
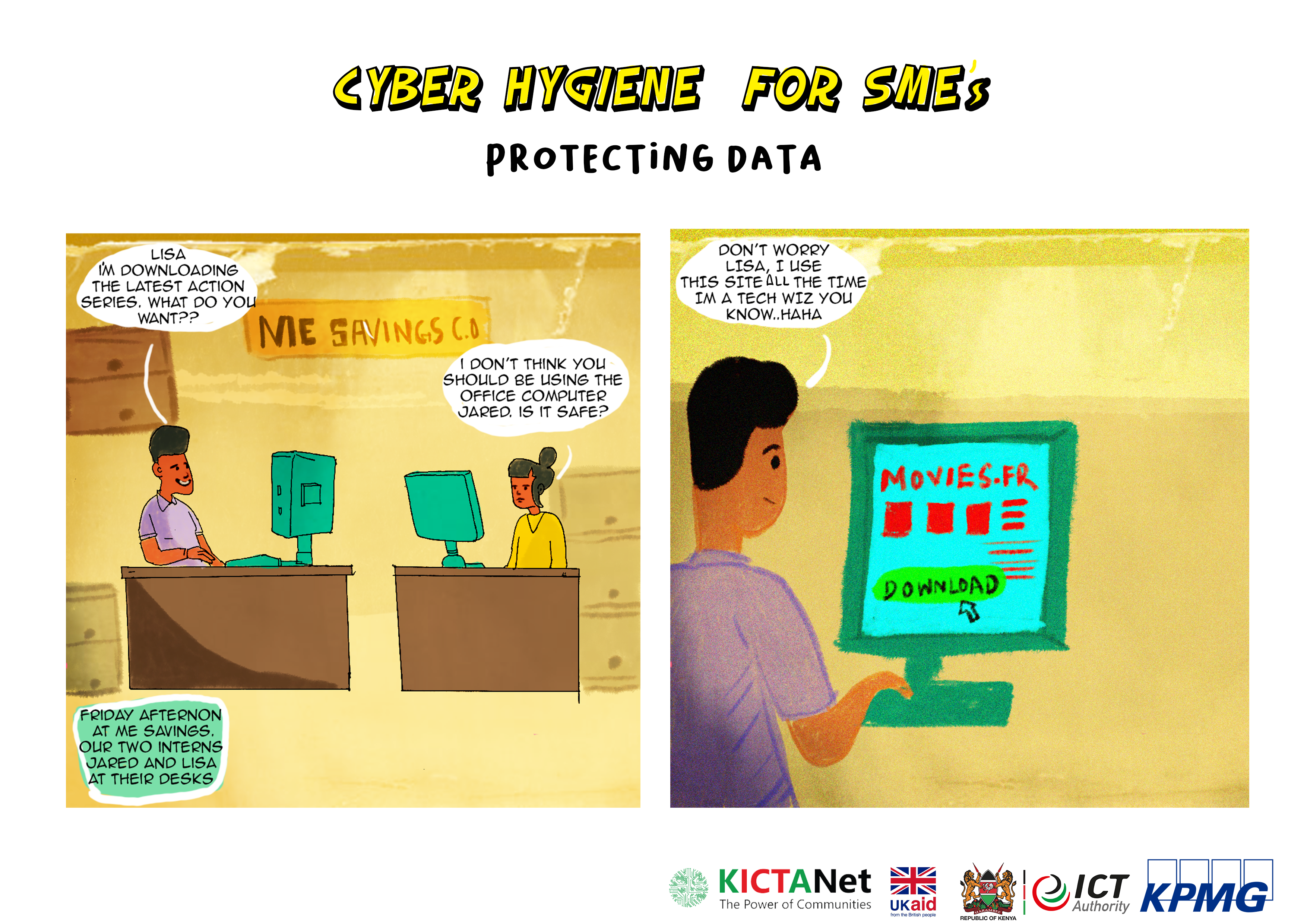
PROTECTING DATA
Identify and classify your sensitive and strategic data.
Classifying your digital data is a fundamental step in implementing effective data protection measures for personal data and intellectual property in a small business. Here are some steps and considerations to help you classify and protect your digital data:
- Start by identifying the different types of data your business handles. Common categories include personal data, financial data, intellectual property, employee data, customer data, and operational data.
- Prioritize data based on its sensitivity and criticality to your business operations. Classify data into categories such as:
- Public: Information that can be openly shared.
- Internal: Restricted to employees within the organization.
- Confidential: Highly sensitive information with restricted access.
- Create a data map that illustrates the flow of data within your organization: Understand where data is stored, processed, and transmitted.
- Consider legal and regulatory requirements relevant to your industry. Certain types of data may have specific compliance requirements, such as Kenya Data Protection and Privacy Act 2019 for personal data or industry-specific regulations.
- Clearly identify and classify your intellectual property, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Understand the value and criticality of each asset.
- Develop and regularly update a comprehensive data inventory: It should list the different data types, their locations, and the purposes for which they are used. Regularly conduct a data audit to ensure that data is appropriately stored and used.
- Implement access controls based on data classification. Limit access to sensitive data to only those individuals who need it for their roles.
- Use encryption for sensitive data, both in transit and at rest. This adds an extra layer of protection, especially for personal data and intellectual property.
- If third-party vendors have access to your data, ensure that they adhere to your data classification and protection standards. Include data protection requirements in vendor contracts.
- Implement robust backup and recovery processes for critical data. Regularly test the recovery procedures to ensure data availability in case of data loss or cyber incidents.
By classifying your digital data and implementing appropriate protection measures, you can enhance the security of personal data and intellectual property within your small business. Regularly review and update your data protection practices to adapt to evolving business needs and cybersecurity threats.
Why data is valuable and is targeted by criminals
Data is valuable for various reasons, and its value has significantly increased with the digital transformation of businesses and the increasing reliance on technology. Criminals target data for several reasons, as it can provide them with opportunities for financial gain, identity theft, espionage, and other illicit activities. Here are some key reasons why data is valuable and attractive to criminals:
- Financial data, such as credit card information, bank account details, and payment credentials, can be directly monetized by criminals. They can use this information for unauthorized transactions, fraud, or selling the data on the dark web.
- Criminals can use stolen identities to commit various crimes, open fraudulent accounts, or apply for loans: Personal information, including names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and birth dates, is valuable for identity theft.
- Businesses generate and store valuable intellectual property, trade secrets, and proprietary information: Cybercriminals or competitors may target corporate data for economic espionage, aiming to gain a competitive advantage or disrupt business operations.
- Ransomware attacks involve encrypting a victim’s data and demanding payment for its release. Criminals know that individuals and organizations often rely on their data and are willing to pay to regain access.
- Login credentials, usernames, and passwords are highly sought after by criminals. Once obtained, these credentials can be used to access various online accounts, compromising personal and professional information.
- Stolen data can be used for various fraudulent activities: Filing false tax returns, obtaining medical services, or creating fake identities.
- The dark web is a marketplace where criminals buy and sell stolen data: Stolen credentials, personal information, and financial data have a market value, making them attractive commodities for cybercriminals.
- Cybercriminals may use sensitive or compromising information to extort money from individuals or organizations. Threatening to expose confidential data can be a powerful means of coercion.
- Nation-states may engage in cyber espionage to steal sensitive government, military, or industrial information for strategic or economic advantages.
- Criminals may target data related to critical infrastructure, such as energy grids or healthcare systems, to disrupt operations and demand ransom payments.
The increasing interconnectedness of our digital world and the sheer volume of sensitive information stored online make data a prime target for criminals. As a result, individuals and organizations must prioritize cybersecurity measures to protect their data from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
Always make a copy of your data and keep the copy in a safe place
For a small business, implementing a cost-effective yet robust data backup strategy is crucial for safeguarding against data loss and ensuring business continuity. Here are some best practices for backing up data and keeping it safe:
- Identify and prioritize critical data that is essential for your business operations. This may include customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and other vital assets.
- Implement automated backup solutions to ensure regular and consistent backups. Automated backups reduce the risk of human error and ensure that data is consistently protected. Keep at least 3 generations of backups, with at least one generation offline (not accessible through the Internet.)
- Choose a reliable and cost-effective backup solution that aligns with your business needs. Options include cloud-based backup services, external hard drives, or network-attached storage (NAS) devices.
- Cloud backup services, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, or dedicated backup providers, offer scalable and affordable solutions. They provide off-site storage, accessibility, and often include features like versioning and file recovery.
- Utilize external hard drives or network-attached storage devices for on-premises backup solutions. These options provide local storage and can be cost-effective for smaller data volumes.
- Adhere to the 3-2-1 backup rule, which recommends having three total copies of your data, stored on two different media, with one copy stored off-site. This rule ensures redundancy and protection against various failure scenarios.
- Implement encryption for sensitive data during the backup process. Encryption adds an extra layer of security, especially for off-site or cloud-based backups.
- Regularly test your backup and recovery processes to ensure that your data can be successfully restored. This practice helps identify any issues before a real data loss event occurs.
- If possible, choose a backup solution that supports versioning. Versioning allows you to restore previous versions of files in case of accidental changes or corruption.
- Ensure that backup storage locations are secure and protected against unauthorized access. This includes both physical and logical security measures.
- Document and regularly update metadata and configuration details related to your backup processes. This documentation is valuable for recovery and system restoration.
- Beyond regular data backup, consider implementing a broader business continuity and disaster recovery plan. This includes strategies for minimizing downtime and ensuring a swift recovery in case of major disruptions.
By following these cost-effective practices, small businesses can establish a reliable and secure data backup strategy to mitigate the risk of data loss and enhance overall resilience. Regularly reviewing and updating backup practices ensures that the strategy remains effective as the business evolves.
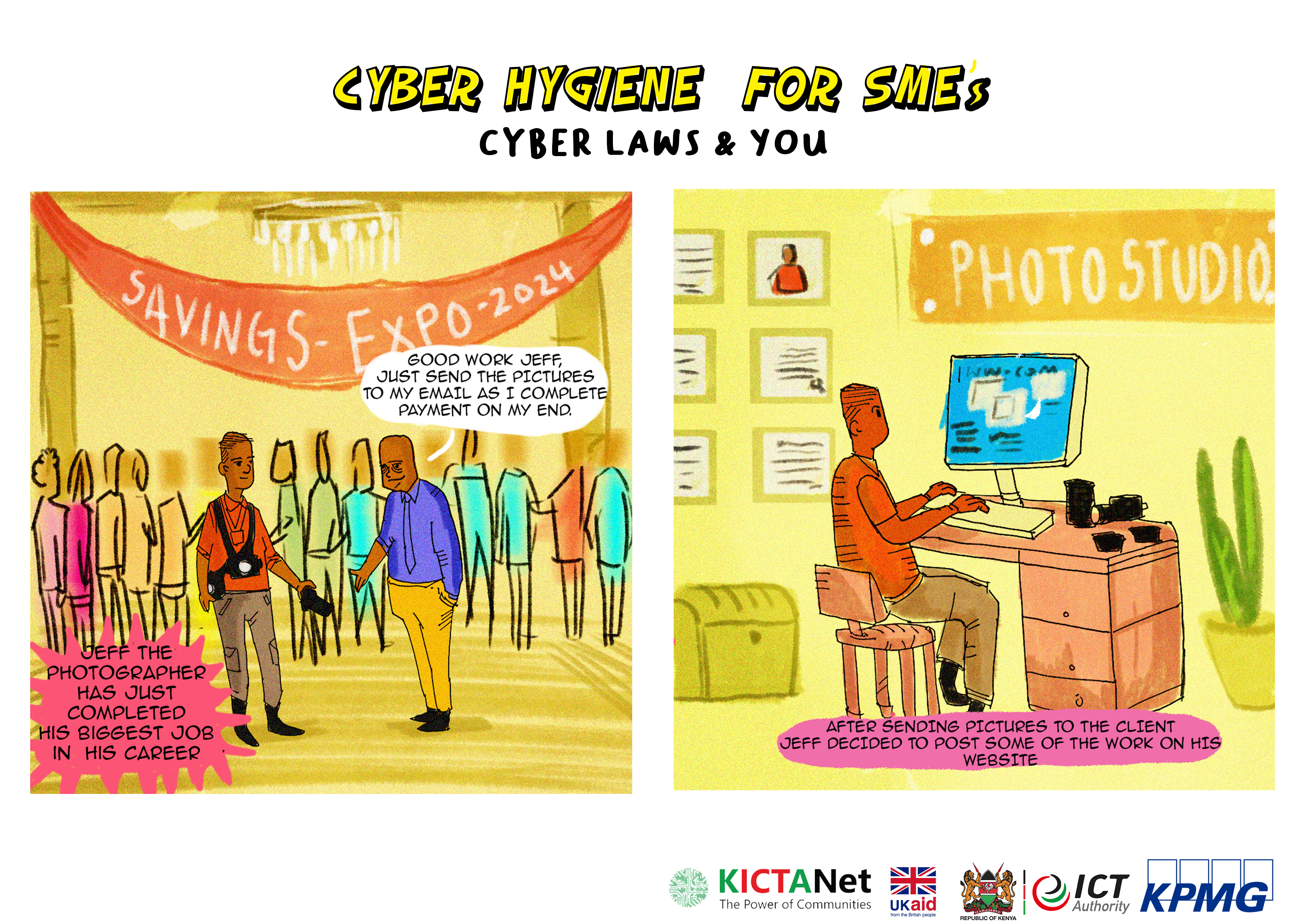
LEGAL COMPLIANCE
Data Protection: Classification, registration, protection.
Kenya’s primary data protection legislation is the Data Protection Act, 2019.
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer if your business processes a significant amount of personal data. The DPO is responsible for ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
- Clearly understand and document the types of personal data your business processes, the purpose of processing, and how long the data will be retained. This is often done through a Data Processing Register.
- Obtain the consent of individuals before processing their personal data. Clearly communicate the purpose for which the data is collected and how it will be used.
- Respect the rights of data subjects, including the right to access, correct, delete, or restrict the processing of their personal data. Have procedures in place to handle such requests.
- Implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This may include encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments.
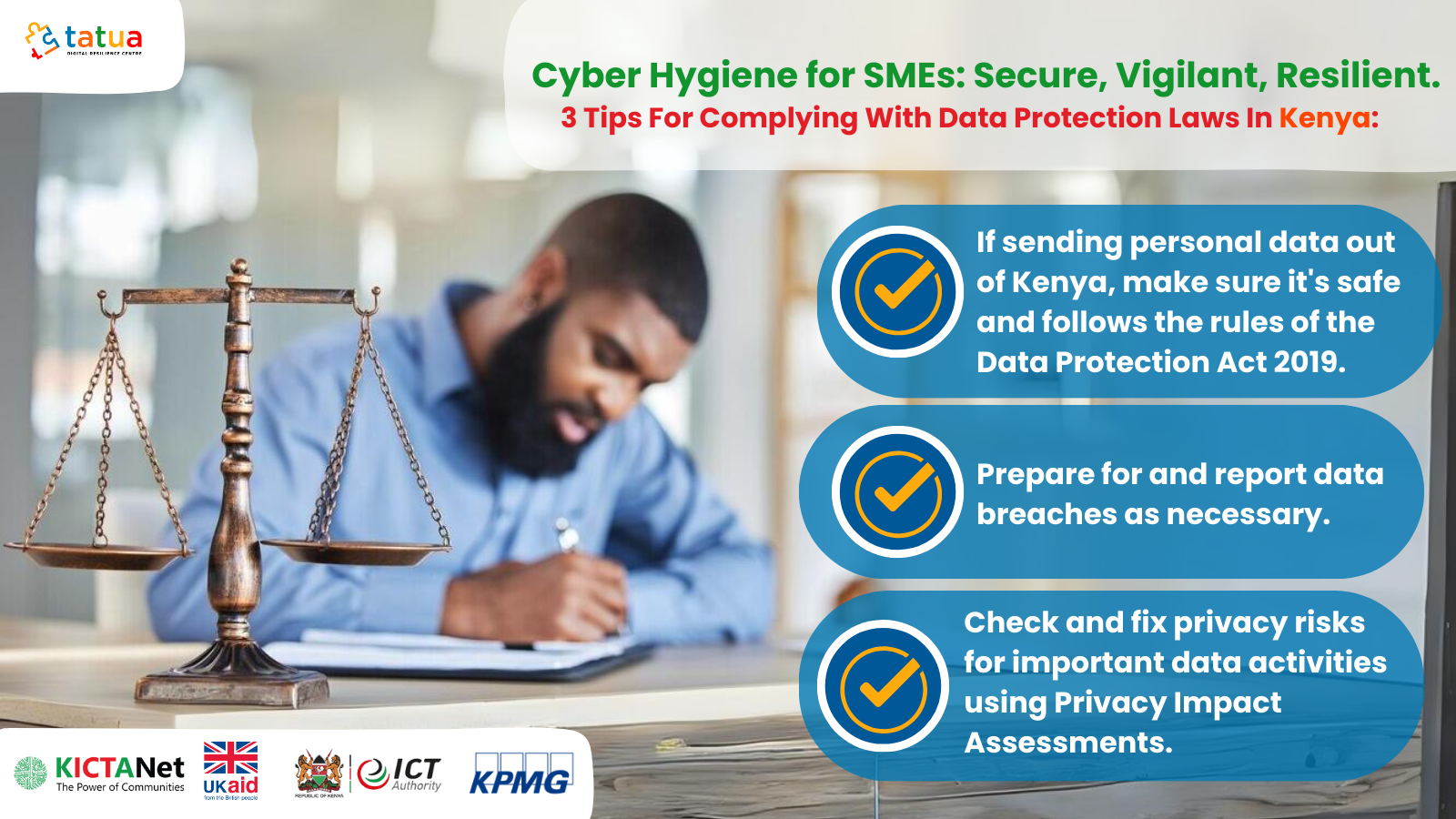
- If transferring personal data outside of Kenya, ensure that adequate safeguards are in place, and the transfer complies with the requirements of the Data Protection Act. (Note that storing personal data in the cloud may constitute a transfer of data outside Kenya)
- Establish procedures for detecting, reporting, and investigating data breaches. If a data breach occurs, notify the relevant authority and affected data subjects as required by the law.
- Conduct Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) for high-risk data processing activities. PIAs help identify and mitigate privacy risks associated with specific projects or processes.
- Ensure that contracts and agreements with third-party data processors include provisions for data protection compliance. Monitor the activities of third parties to whom you entrust personal data.
- Provide training to employees on data protection principles and compliance requirements. Employees should be aware of their responsibilities in handling personal data.
- Maintain records of data processing activities, security measures, and data protection impact assessments. This documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance.
- Cooperate with and respond to requests from the Data Commissioner, who is responsible for enforcing the Data Protection Act in Kenya.
- Consultation with legal professionals familiar with Kenyan data protection laws is highly recommended to ensure accurate compliance.
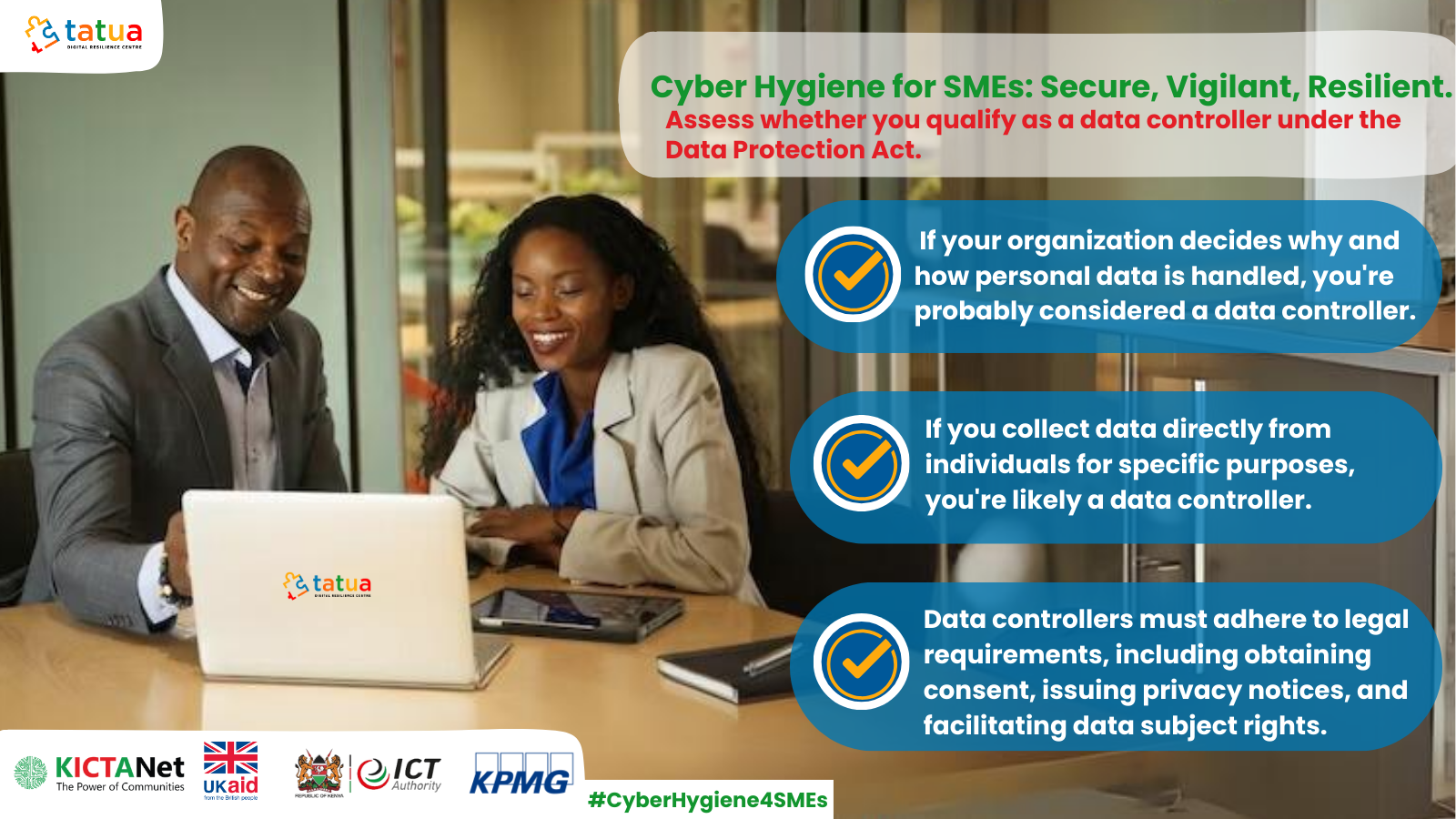
Is your enterprise a data controller or a data processor?
In the context of data protection laws, including the Data Protection Act, 2019 in Kenya, it’s essential to understand the roles of a data controller and a data processor. These roles determine the responsibilities and obligations of entities involved in the processing of personal data:
- Data Controller: A data controller is an entity that determines the purposes and means of processing personal data. In other words, the data controller is the entity that decides why and how personal data should be processed. The controller is primarily responsible for complying with data protection laws and ensuring that processing activities are lawful, fair, and transparent. Under the Kenya Data Protection Act, consider the following:
- Decision Making Authority: If your organization determines the purposes and means of processing personal data, you are likely a data controller.
- Direct Interaction with Data Subjects: If you directly interact with individuals and collect their data for specific purposes defined by your organization, you are likely a data controller.
- Obligations under the Data Protection Act: Data controllers have specific obligations under the law, including obtaining consent, providing privacy notices, and facilitating data subject rights.
- Data Processor: A data processor, on the other hand, is an entity that processes personal data on behalf of the data controller. Processors act on the instructions of the controller and are responsible for ensuring the security and proper handling of the data during processing. Under the Kenya Data Protection Act, consider the following:
- Processing on Behalf of Another Entity: If your organization processes personal data based on the instructions of another entity (the data controller), you are likely a data processor.
- Limited Decision-Making Authority: Data processors typically have limited decision-making authority regarding the purposes and means of processing. They act as per the instructions of the data controller.
- Contractual Relationship: If there is a contractual agreement between your organization and another entity specifying that you are processing data on their behalf, you are likely a data processor.
NOTE: It’s important to note that in some cases, an entity may act as both a data controller and a data processor depending on the context of a specific processing activity. Seeking legal advice specific to your situation is recommended for a thorough understanding of your obligations under the law.
If you are a data controller or processor, register with the data commissioner.
Here are the general steps you may follow to register with the Data Commissioner in Kenya:
- Start by visiting the official website of the Data Protection Commissioner in Kenya. Look for the latest information on data protection registration requirements and processes.
- Read and understand the registration guidelines provided by the Data Commissioner. These guidelines typically outline the categories of data controllers that are required to register, registration fees, and the information/documentation needed for registration.
- Collect the necessary information and documents for registration. This may include details about your organization, the types of personal data you process, the purposes of processing, security measures in place, and contact information.
- Fill out the registration form provided by the Data Commissioner. This form will likely include details about your organization’s data processing activities and the measures you have in place to protect personal data.
- Check for any applicable registration fees and ensure they are paid. Registration fees may vary depending on the size and nature of your organization.
- Submit the completed registration form along with any required documents to the Data Commissioner. This can often be done electronically through the commissioner’s online portal.
- Upon successful submission, you may receive an acknowledgment or confirmation of your registration. This acknowledgment may include a registration number or other reference information.
- Once registered, it is crucial to maintain compliance with data protection laws. This includes implementing and regularly reviewing data protection policies, ensuring the security of personal data, and cooperating with the Data Commissioner’s office.
Ensure that personal data is stored securely.
Securing personal data is crucial for small companies to comply with data protection laws and to protect the privacy of individuals. Here are some guidelines for securely storing other people’s personal data:
- Conduct a thorough inventory of the personal data your company collects and processes. Clearly document what types of data you hold, the purposes for which you collect it, and how long you plan to retain it.
- Only collect the personal data that is necessary for the specified purposes. Avoid collecting excessive information that is not relevant to your business operations.
- Restrict access to personal data to only those employees who need it for their job responsibilities. Implement role-based access controls to ensure that employees only have access to the data necessary for their roles.
- Encrypt sensitive personal data, both in transit and at rest. This provides an additional layer of protection in case of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Choose secure storage solutions for your data, whether it’s on-premises or in the cloud. Ensure that the chosen platform complies with data protection standards and offers robust security features.
- Implement regular data backup procedures to prevent data loss in case of accidental deletion, hardware failure, or other unforeseen events. Store backups securely and test the restoration process periodically.
- Develop and enforce security policies within your organization. These policies should cover aspects such as password management, employee training, and acceptable use of company resources.
- Provide regular training to employees on data protection principles and security best practices. Ensure that they understand the importance of safeguarding personal data and recognize potential security threats.
- Develop an incident response plan to address data breaches or security incidents promptly. Outline the steps to be taken, including notification procedures, to mitigate the impact of a breach.
- Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities in your data storage and processing systems. This proactive approach helps prevent security incidents.
- Establish clear policies for data retention and disposal. Only retain personal data for as long as necessary, and securely dispose of data that is no longer needed.
- Stay informed about and comply with relevant data protection laws and regulations, including the Data Protection Act in Kenya. Regularly review your data protection practices to ensure ongoing compliance.
Do not falsely advertise through your digital channels.
False advertising is considered a breach of law in Kenya! If you make false claims through your online channels or advertise goods or services that you do not provide, you may be in breach of law.
Key provisions related to false advertising and consumer protection under the Consumer Protection Act in Kenya, 2012, include:
- The Act prohibits making false or misleading representations regarding the characteristics, benefits, or suitability for a purpose of any goods or services. This includes false advertising that could deceive or mislead consumers.
- The Act contains provisions against engaging in unfair practices that are likely to take advantage of consumers. False advertising falls within the scope of unfair practices.
- The legislation requires accurate and clear labeling of products, including information provided in advertisements. Misleading information about products or services could constitute a violation.
- The Act addresses consumer contracts and prohibits terms that are unfair or misleading. Any false representations made in the context of consumer contracts could be considered a breach of the law.
- Regulatory authorities, such as the Competition Authority of Kenya, are responsible for enforcing consumer protection laws. The Act outlines penalties for violations, including fines and other remedies.
- To ensure compliance with advertising and consumer protection laws in Kenya, businesses should:
- Provide accurate and truthful information about their products or services.
- Avoid making false or misleading representations in advertisements.
- Clearly communicate the terms and conditions of transactions.
- Comply with labeling requirements for products.
- Respond promptly and appropriately to consumer complaints.
Businesses should also stay informed about any updates or amendments to the relevant laws to ensure ongoing compliance. Legal advice from professionals familiar with Kenyan consumer protection laws can provide specific guidance based on the nature of the advertising practices in question.
PROTECTING YOUR PEOPLE
Check the reputation of all IT vendors before you procure their goods and services.
Not all device and application vendors are reliable and trustworthy. Check every vendor from whom you intend to procure technology goods or services.
- Research the company’s website and social media pages. Pay attention to the company’s history, mission, and values.
- Check customer reviews and testimonials. Websites like Trustpilot, Google Reviews, or industry-specific forums can provide insights into the experiences of other customers.
- Ask for references from previous or current clients who can share their experiences with the products, services and the specific vendor.
- Check the vendor’s credentials and certifications. Reputable ICT vendors often have certifications relevant to their industry. For example, if they provide cybersecurity solutions, they may have certifications from organizations like ISO, ISACA, CREST, or others.
- Look for partnerships with well-known and established companies or organizations in the industry and active participation in industry conferences and events.
- Assess the responsiveness and quality of customer support. Contact the vendor’s customer support with any questions you may have and evaluate their communication and problem-solving abilities.
- Assess Financial Stability of the vendor. A financially stable company is more likely to provide consistent and reliable services. Check company annual reports or third-party sources for this information.
- Carefully review the terms and conditions in contracts and SLAs. Ensure that they align with your expectations and clearly define the responsibilities and obligations of both parties.
- Question the vendor about robust security measures in place and compliance with laws such as data protection laws.
- Check for red flags such as unprofessional communication, inconsistent information, or a lack of transparency. Investigate further if you feel uncomfortable. Seek competent legal advice regarding any contracts or agreements, before signature.
Explain the importance of strong passwords to your clients
Your clients’ accounts and your systems can be compromised if their passwords can be easily hacked. Ensure that your clients are trained to observe the following in password design:
- 12 Characters long or longer.
- Mixed characters: Letters and numbers;Uppercase and lowercase; Include special characters.
- Be unique: avoid common words and phrases, names, birthdays and any information that can easily be related to you.
- Don’t maintain default passwords, always change to a unique password immediately.
- Use unique phrases that you can remember.
- Create a unique password for different accounts.
- Regularly update passwords.
- Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords. Password managers can help you create unique, strong passwords for each account without the need to remember them all.
- Beware of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of phishing attempts that try to trick you into revealing your password. Always verify the legitimacy of the website or email before entering your password.
- Check for Breaches: Periodically check if your passwords have been involved in data breaches. Websites like Have I Been Pwned can provide information on whether your passwords have been compromised.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Whenever possible, enable multi-factor authentication for your accounts. This adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password.
Remember that the goal is to create a password that is difficult for others to guess but easy for you to remember.
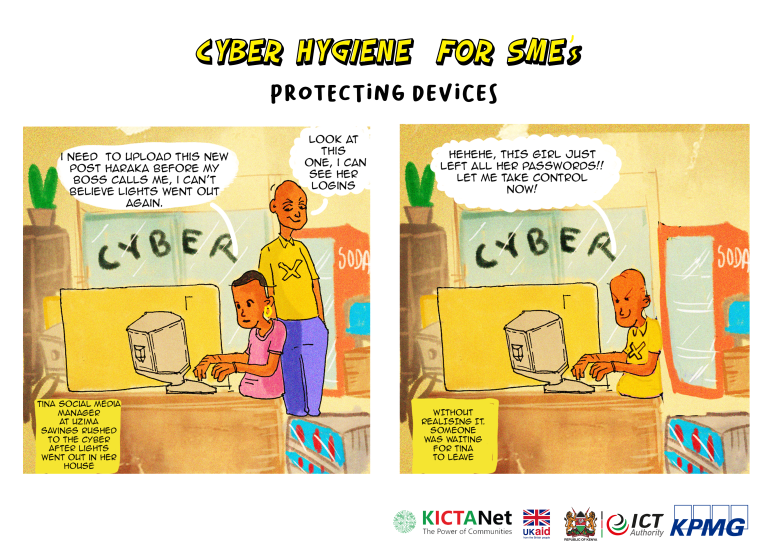
Tell your users never to share personal information (e.g. PIN and password) with others.
The easiest way for a criminal to get a password is to trick the password owner into giving it to him or her. Train your clients never to disclose their passwords.
- Do Not Share Your Passwords with anyone, including friends, family, colleagues or service providers.
- Avoid using the same password for different accounts.
- Regularly change passwords, especially for your sensitive accounts.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links in emails or messages that request your login credentials. Always verify the legitimacy of any website or application before entering your password.
- If you need to write down passwords, store the information securely in a location that only you can access.
- Whenever possible, enable two-factor authentication for your accounts. This adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password, requiring an additional verification step.
- Consider using a reputable password manager to generate, store, and manage complex passwords.
- Regularly monitor your accounts for any suspicious activity. Check your account activity logs and review notifications from the services you use.
- If you are aware of a security incident or if a service you use has been compromised, change your password for that service immediately.
- Stay informed about current security best practices. Be aware of the latest threats and security measures to better protect your accounts.
- Periodically check if your passwords have been involved in data breaches. Websites like Have I Been Pwned can provide information on whether your passwords have been compromised.
- Ensure that your account recovery options (such as email addresses or phone numbers) are up-to-date. This can help you regain access to your account if you ever forget your password or get locked out.
How can I protect myself from becoming a victim of SIM Swap?
What is a SIM swap?
SIM swapping is a type of cyber crime where a criminal fraudulently convinces a telecommunications company to transfer a victim’s phone number to a SIM card under the criminal’s control. This involves tricking customer service into associating the victim’s phone number with a new SIM card owned by the criminal. Once a criminal successfully carries out a SIM swap, they gain control over the victim’s phone number, which can lead to various malicious activities such as:
- Unauthorized access to applications such as email, social media and financial accounts.
- Resetting and changing the victim’s device and application passwords.
- By gaining complete control over the victim’s device the criminal is able to steal the victim’s identity and perform all the functions that the rightful owner can normally carry out. Thus the criminal can carry out financial fraud, social engineering attacks targeting the victim’s contacts and diversion of communications to the criminal’s own devices.
- The criminal may use the compromised accounts to gather personal information about the victim, leading to potential identity theft or other forms of fraud.
How can you protect yourself from becoming a victim of a SIM swap scam?
- Activate anti-SIM swap technology on your device. This involves dialling a USSD code provided by your telecommunications provider. Search for the correct code on their official website or contact customer service for guidance.
- Secure your device with a PIN or password.
- Regularly monitor your accounts for any suspicious activity and immediately report any concerns to your telecommunications provider.
- Check for SIM Lock or SIM PIN which is a password which must be entered when a device is restarted or when a SIM is inserted into a new device.
- Keep informed on recent social engineering tactics, in particular, do not share your device, passwords or personal information that is useful to criminals.
- Keep in touch with your telecommunications provider and make sure that your contact information such as your email address is up to date. Regularly check for notifications from your provider.
- Report lost or stolen devices immediately so that your provider can take steps to prevent unauthorized access to your account.
- Note that the details of activating protection can vary by provider and by country or region. Ensure that you know the ones for your current status.
SAFEGUARDING DIGITAL MONEY
Avoid transacting money when using public WiFi
Performing online financial transactions over open, public WiFi connections poses significant cybersecurity risks due to the inherent lack of security controls on such networks. Here are some reasons why it’s considered a bad idea and tips on achieving better cybersecurity protection in such scenarios:
Risks of Online Financial Transactions on Public WiFi:
- Man-in-the-Middle Attack: Public WiFi networks are susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker intercepts communication between your device and the network. This can lead to the theft of sensitive information, including financial data.
- Unsecured Networks: Public WiFi networks often present information in plain text (unencrypted), making it easier for attackers to eavesdrop on the data transmitted between your device and the network.
- Rogue Hotspots: Cyber criminals can set up rogue WiFi hotspots with names similar to legitimate public networks. Users may unknowingly connect to these malicious hotspots, allowing attackers to monitor and capture data.
- Untrustworthy Network Infrastructure: Public networks may not employ robust security measures. The configuration settings may have been altered or the network infrastructure itself may be compromised with illegitimate hardware devices, or manipulated by attackers to gain unauthorized access to user data.
- Session Hijacking: Attackers may use session hijacking techniques to take over an active session between your device and a financial website. This can lead to unauthorized access and transactions.
Tips For Better Digital Security:
- Avoid carrying out Sensitive Transactions: Refrain from conducting sensitive financial transactions, such as online banking or shopping, on public WiFi networks. Save such activities for trusted, secure networks.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for your financial accounts. Even if login credentials are compromised, 2FA adds an additional layer of security by requiring a second verification step.
- Use Secure Websites (HTTPS): Ensure that the websites you access for financial transactions use HTTPS. Look for the padlock icon in the address bar, indicating a secure connection.
- Turn Off Sharing: Disable file and printer sharing, as well as public folder sharing, on your device to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Forget the Network After Use: After using a public WiFi network, forget the network on your device to prevent automatic connections in the future. This minimizes the risk of connecting to a rogue hotspot with a similar name.
- Update Software and Apps: Keep your device’s operating system, browsers, and security software up to date. Regular updates patch vulnerabilities and enhance overall security.
- Use a Firewall: Enable a firewall on your device to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. This adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Disable Automatic WiFi Connectivity: Turn off the automatic connection to WiFi networks on your device. Manually select and connect to trusted networks when needed.
- Monitor Account Activity: Regularly monitor your financial accounts for any suspicious activity. Report any unauthorized transactions to your financial institution immediately.
- Consider Using Your Mobile Phone’s hotspot: Using a personal mobile hotspot or tether your device to your smartphone’s cellular data connection is better than relying on public WiFi.
- Educate Employees about the risks and best practices for secure connectivity when work-related tasks in public spaces.
- Use Virtual Private Network (VPN): Employ a reputable VPN service to encrypt your internet connection. A VPN creates a secure tunnel for your data, reducing the risk of eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. However, it’s important to choose a reputable and trustworthy VPN service to ensure the effectiveness of the encryption and protect against potential privacy concerns.
Benefits of a Virtual Private Network (VPN):
- Encryption of Data: A VPN encrypts the data transmitted between your device and the VPN server. This encryption helps protect sensitive information, including login credentials, financial data, and personal details, from being intercepted by malicious actors on the same WiFi network.
- Privacy Protection: VPNs mask your IP address and provide a level of anonymity by routing your internet traffic through a server in a different location. This helps protect your privacy and makes it more challenging for attackers to track your online activities.
- Securing Online Transactions: When conducting online financial transactions, the encrypted connection provided by a VPN adds an extra layer of security. This is especially important when using public WiFi, where the risk of data interception is higher.
- Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: VPNs can mitigate the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks by encrypting data and making it more difficult for attackers to intercept or manipulate the communication between your device and the internet.
- Secure Remote Access: For businesses, VPNs provide a secure way for employees to access corporate networks and sensitive data remotely. This is crucial for maintaining security, especially when employees connect to public WiFi while working on the go.
- Geo-Spoofing: VPNs allow users to select servers in different geographic locations. This feature helps in geo-spoofing, making it appear as though your internet connection is originating from a different location, enhancing privacy and security.
By implementing these cybersecurity measures, individuals can better protect themselves from the inherent risks associated with online financial transactions on public WiFi networks. The goal is to create layers of defense that reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access and data compromise.
Don’t follow instructions for sending and receiving money that are not issued by your service provider.
When using online and mobile money wallets, it’s crucial to prioritize security to protect your financial information and transactions. Here are some simple security measures you should take:
- Use Strong Authentication: Enable and use strong authentication methods, such as PIN codes, passwords, or biometrics (fingerprint or facial recognition). Avoid using easily guessable or common passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Whenever possible, enable two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security. This typically involves receiving a one-time code on your mobile device for verification.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update the mobile wallet app and your device’s operating system. Software updates often include security patches that protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Download Financial Apps from Official Stores: Only download mobile wallet apps from official app stores (such as Google Play or the Apple App Store). Avoid third-party app sources or unofficial websites which have been accessed through conducting an Internet search to reduce the risk of downloading malicious software.
- Check the name of the official wallet application with your service provider. Do not use any financial application that is described as a “Beta” version.
- Secure Your Device: Use a PIN, password, or biometric authentication to secure your mobile device. Ensure that your device auto-locks after a period of inactivity.
- Use Secure Wi-Fi Connections: Avoid conducting financial transactions over public Wi-Fi networks. If you must use public Wi-Fi, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for added security.
- Regularly Check Transactions: Monitor your wallet transactions regularly. Report any unauthorized or suspicious transactions to the mobile wallet provider immediately.
- Always check your balance after a transaction.
- Download and save transaction notifications and download and save a full statement from your wallet at least once a month.
- Protect sensitive Personal or Business Information: Be cautious about sharing sensitive information linked to your mobile wallet or saving it on devices or documents which can be accessed by other people. Avoid storing sensitive data like passwords or PINs in easily accessible locations.
- Review App Permissions: Review and manage the permissions granted to the mobile wallet app. Only grant necessary permissions to ensure the app functions properly without excessive access to your device’s features.
- Secure Your Email Account: Ensure that the email account associated with your mobile wallet is secure. Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and regularly monitor for suspicious activity.
- Logout When Not in Use: Always log out of your mobile wallet app when you’re not using it. This adds an extra layer of protection, especially if your device falls into the wrong hands.
- Educate Staff and Partners: Stay informed about the security features and best practices provided by your mobile wallet provider. Familiarize yourself with their policies on fraud protection and account recovery.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of phishing attempts through emails, text messages, or calls. Mobile wallet providers typically communicate important information through secure channels within the app.
- Use Lost or Stolen Device Features: Familiarize yourself with features that allow you to remotely lock or wipe your device in case it’s lost or stolen. Mobile operating systems often include these security measures.
- Secure Your Backup and Recovery Options: If the mobile wallet offers backup and recovery options, ensure that they are secured with strong authentication. Be cautious about storing recovery information in easily accessible locations.
- Do not respond to requests for reversal until you have checked your balance and transaction log. (e.g. Safaricom forward the message to 456)
Implementing these simple security measures can significantly enhance the safety of your online and mobile money wallet transactions. Regularly reviewing and updating your security practices ensures that you stay protected against evolving threats.
Confirm details twice before completing a financial transaction.
Building the habit of checking your online financial transactions before completing them is a crucial step in ensuring the security and accuracy of your financial accounts. Here are some strategies to help you develop and maintain this habit:
- Set Regular Transaction Review Times: Schedule specific times during the week to review your financial transactions. This could be a weekly or bi-weekly routine. Consistency is key in forming a habit.
- Use Transaction Alerts: Enable transaction alerts from your bank or financial institution. Receive notifications for every transaction, and set them up to alert you for both large and small amounts. This helps you stay informed in real-time.
- Assign responsibility to a staff member within your accounting function to manage transaction alerts and guide the staff member what to do in the event of an anomaly
- Use Financial Management Apps: Explore financial management apps that aggregate transactions from multiple accounts. These apps often categorize expenses and provide a clear overview, making it easier for you to review your financial patterns
- Make financial reviews a corporate activity: Use visual cues or reminders. Set up calendar events, place sticky notes on devices, or use smartphone reminders to prompt staff to keep tabs on financial transaction
- Make transaction reviews a collaborative effort. Set aside time together to go through transactions, discuss budgets, and identify any discrepancies.
- Establish a routine that includes checking your financial transactions. Whether it’s the first thing you do in the morning or the last thing before bed, having a consistent routine makes it easier to remember.
- Process organizational financial data to identify your financial patterns and train staff to quickly recognise anomalies
- Create a checklist of steps to follow during your transaction review. Having a systematic approach can make the process more manageable and less overwhelming.
- Implement rewards: Create a reward system for staff review of financial transactions and, especially, recognition of anomalies. This will encourage staff to expose scams.
- Educate Yourself on Common Scams: Stay informed about common scams and fraudulent activities. Knowing the signs of potential fraud can increase your vigilance during transaction reviews.
- Set Goals and Stay Accountable: Set goals for implementing procedure and reducing financial errors and frauds. Communicate these goals to people in your organization and design rewards for achievement.
- Incorporate the achievement of these goals into staff performance reviews.
- Communicate the benefits of financial prudence: Regularly communicate the benefits of good financial practice to staff.
- Communicate success and recognize achievements.
MANAGING YOUR BRAND AND REPUTATION
Own and personally register your online presence.
Outsourcing domain name registration can be convenient for small businesses, but it does come with certain risks. Here are some risks associated with outsourcing domain registration and tips on how small businesses, particularly in third-world countries, can protect themselves:
Risks of allowing a third party (for example your web hosting company) to register your domain name:
- You may lose control of your domain and need the permission and help of your host to make any changes.
- If your host does not enforce best practices, there may be security vulnerabilities on your website that enable unauthorized access, domain hijacking, or other security breaches.
- If the third party’s contact information is associated with your domain you may have difficulty regaining ownership and control of the domain in the case of a dispute.
- If the third party is maintaining the account, you may not have visibility on:
- Whether the renewal fees are being regularly paid and therefore your domain may expire!
- Issues that are being raised by your customers about your domain and inadequate customer assistance and support may affect your reputation.
- Any illegal activities associated with your domain
How to Mitigate The Risks of IT Outsourcing
- Select reputable and well-known domain registrars with a history of good customer service and security practices. Check reviews and ask for recommendations from trusted sources.
- Ensure that your official business contact information is used for domain registration. This includes the business’s email address and contact details. This helps maintain ownership rights.
- Ensure that your business owns and regularly updates the top level login details for the domain registrar account. Enable two-factor authentication on the domain registrar account for an additional layer of security. This helps protect against unauthorized access.
- Set up reminders for domain renewal dates and regularly monitor the status of the domains. Be proactive about renewing domains to prevent accidental expiration.
- Read and understand the terms and conditions of the domain registrar. Be aware of the renewal process, transfer policies, and any potential fees associated with domain management.
- Maintain detailed records of domain registration, including login credentials, registration details, and renewal dates. This documentation is crucial for resolving disputes or transferring domains.
- Periodically review and audit the domain settings to ensure that the correct contact information, name servers, and other configurations are in place.
- If entering into a contract with a third-party registrar, ensure that the terms are clear, especially regarding ownership, renewal responsibilities, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Ensure that the email account associated with the domain registrar is secure. This email is often used for communication and password recovery, so it’s essential to protect it.
- Develop a plan for transferring domains to another registrar if needed. This plan should include steps for resolving any disputes or issues that may arise during the transfer process.
By carefully selecting a reputable registrar and implementing these protective measures, small businesses can mitigate the risks associated with outsourcing domain name registration. Regular monitoring and proactive management are key to maintaining control and security over domain assets.
Beware that up to 5 billion people can see you on the internet.
The visibility of a message posted on a social media platform can vary widely depending on several factors, including the platform’s settings, the user’s privacy choices, and the nature of the content. Here are some considerations and tips for understanding and managing the visibility of social media posts:
Factors Affecting Visibility:
- Most social media platforms offer privacy settings that allow users to control who can see their posts. Users can typically choose between options like public, friends only, or a custom setting.
- Social media algorithms determine the visibility of posts on users’ feeds. The more engagement a post receives (likes, comments, shares), the more likely it is to be shown to a larger audience.
- If a post is set to “public” or includes popular hashtags, it can be seen by a broader audience beyond the user’s immediate connections.
- Interactions with other users’ content, such as comments or likes, can increase the visibility of one’s own posts within specific social circles.
Tips for Managing Visibility:
- Regularly review and adjust privacy settings on social media platforms. Be aware of who can see your posts and adjust settings based on your comfort level.
- Exercise caution when posting content publicly, especially if it contains sensitive information. Consider using private settings for more personal or sensitive updates.
- Use custom audience settings to control who sees specific posts. This allows for a more tailored approach to sharing content with different groups of connections.
- Avoid sharing too much personal information publicly. Be mindful of the details you reveal, and consider whether information could be used maliciously.
- Understand the features of the social media platform you’re using. Some platforms provide additional tools, such as friend lists or close friends’ options, to further control audience visibility.
- Many platforms offer an activity log where users can review their interactions, posts, and privacy settings. Regularly check the activity log to ensure that your content is being shared as intended.
- Protect your account by using strong, unique passwords and enabling two-factor authentication. This helps prevent unauthorized access to your social media accounts.
- Stay informed about platform updates and changes to privacy settings. Social media platforms may evolve, and being aware of these changes is essential for maintaining control over your online presence.
Remember that maintaining privacy and controlling the visibility of your content is an ongoing process. Regularly reviewing and adjusting settings based on your preferences and the nature of your content can help you manage your online presence effectively.
PROTECTING YOUR NETWORK
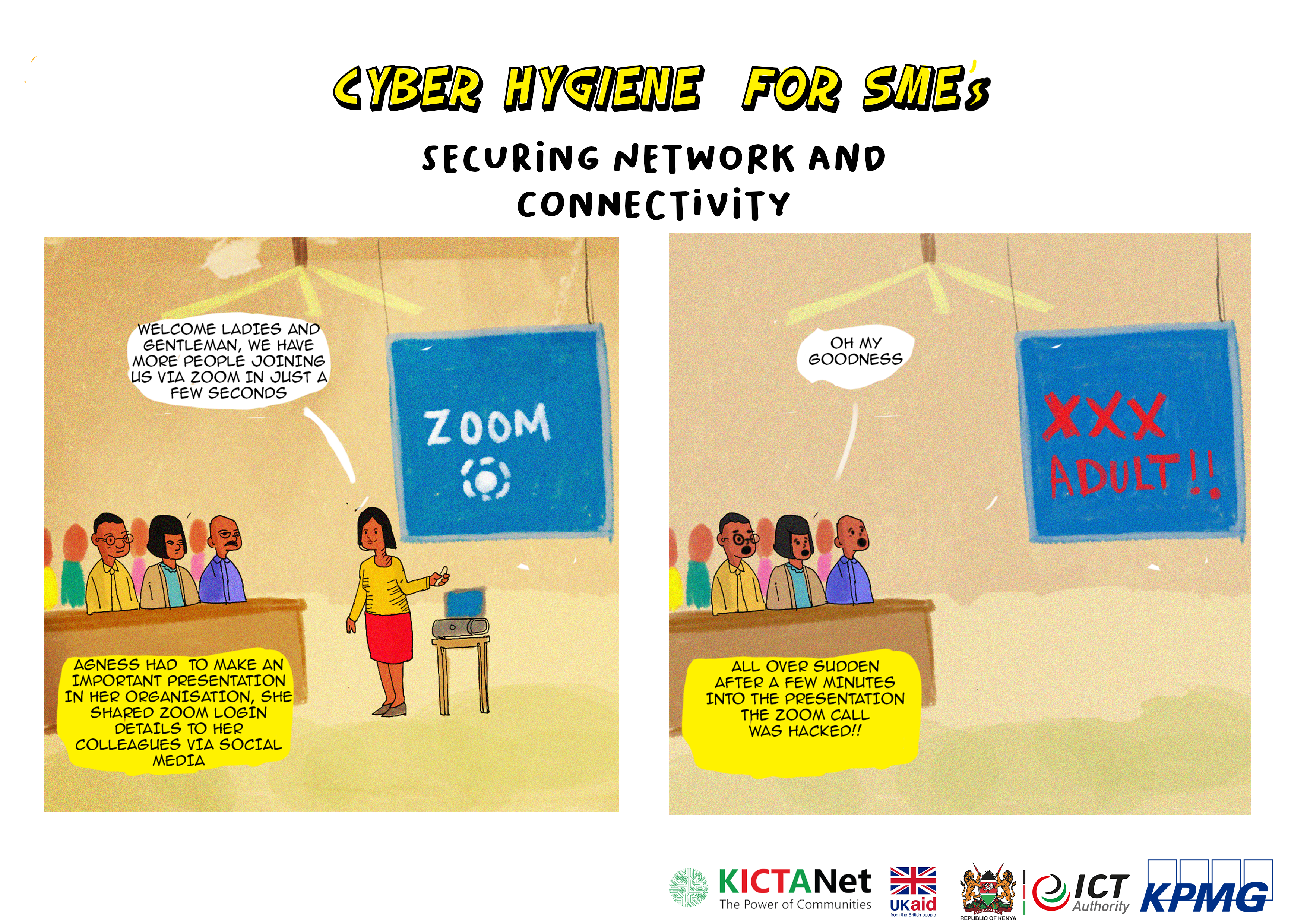
Protect your teleconferences
Ensuring the security of online meetings for a small business is crucial to protect sensitive information and maintain the confidentiality of discussions. Here are steps you can take to hold a secure online meeting:
- Choose a Secure Platform: Select a reputable and secure online meeting platform. Look for features such as end-to-end encryption, password protection, and robust security protocols. Popular choices include Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, and Cisco Webex.
- Use Meeting Passwords: Enable password protection for your meetings. This adds an additional layer of security by requiring participants to enter a password before joining. Share the password securely with authorized attendees.
- Generate Unique Meeting IDs: Avoid using personal meeting IDs for public or large meetings. Instead, use randomly generated meeting IDs for each session. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access through the reuse of IDs.
- Enable Waiting Rooms: Utilize the waiting room feature to control who enters the meeting. This allows the host to admit participants individually, preventing unauthorized individuals from joining.
- Restrict Screen Sharing: Limit screen-sharing capabilities to the host or trusted participants. This prevents accidental or malicious sharing of sensitive information during the meeting.
- Update Software Regularly: Keep the online meeting platform and any associated plugins or applications up to date. Regular updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities.
- Use Virtual Backgrounds Carefully: If your platform supports virtual backgrounds, be cautious about using sensitive or confidential information as your background. Ensure that no unintended information is visible during the meeting.
- Educate Participants: Provide guidelines to participants on best practices for secure online meetings. Encourage them to join from secure environments, avoid sharing meeting links publicly, and use unique passwords.
- Secure Meeting Recordings: If you record the meeting, ensure that the recording is stored securely. Limit access to the recording and consider using password protection for recorded content.
- Monitor Participants: Be attentive to the list of participants during the meeting. If you notice any unfamiliar individuals, remove them promptly and take appropriate action to maintain security.
- Disable Unnecessary Features: Disable any unnecessary features or settings that could pose security risks. For example, if your meeting does not require file sharing, disable this feature to reduce potential vulnerabilities.
- Use Encryption: Ensure that the online meeting platform uses encryption to protect the data transmitted during the meeting. Look for platforms that offer end-to-end encryption for enhanced security.
- Set Clear Security Policies: Establish and communicate clear security policies for online meetings. Include guidelines on acceptable behavior, data sharing, and consequences for violating security protocols.
- Regularly Review Security Settings: Periodically review and update security settings based on the evolving security landscape. Stay informed about new features and settings provided by the platform to enhance security.
- Consider Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If the online meeting platform supports it, enable two-factor authentication for additional user verification. This adds an extra layer of protection to account access.
- Have a Contingency Plan: Develop a contingency plan in case of security incidents. Know how to address disruptions, unauthorized access, or other security issues swiftly and effectively.
By implementing these measures, a small business can enhance the security of its online meetings, safeguard sensitive information, and create a more secure virtual collaboration environment. Regularly updating security practices and staying informed about the features offered by the chosen platform contribute to ongoing security.
Require staff to use a VPN to log onto sensitive corporate system
Setting a policy for staff to always use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when logging on to sensitive corporate systems is a crucial step in enhancing the security of your organization’s data and communications. Here’s a guide on how to establish and communicate such a policy:
- Define the Policy Objectives: Clearly outline the objectives of implementing a VPN policy. This may include securing data transmission, protecting against potential threats, and ensuring a secure connection to sensitive corporate systems.
- Identify Sensitive Systems and Data: Clearly define which corporate systems and types of data are considered sensitive and require the use of a VPN. This could include databases, internal servers, communication tools, or any system that handles confidential information.
- Communicate the Importance of VPN Use: Communicate to your staff why using a VPN is crucial for maintaining the security and privacy of sensitive corporate information. Emphasize the potential risks associated with accessing sensitive systems without a secure connection.
- Provide Training and Education: Offer training sessions to educate your staff on the proper use of VPNs. Explain how to install, configure, and activate the VPN, and provide guidance on troubleshooting common issues. Ensure that employees understand the benefits of using a VPN and are aware of potential security threats.
- Select a Reliable VPN Solution: Choose a reliable and secure VPN solution for your organization. Ensure that the selected VPN service offers encryption, follows industry best practices, and complies with relevant security standards. Test the VPN solution thoroughly before implementation.
- Include VPN Use in Security Policies: Integrate the VPN policy into your organization’s overall security policies. Ensure that VPN use is consistent with other security measures, such as password policies, access controls, and data encryption standards.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Consider implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) in conjunction with VPN use. MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, enhancing access controls for sensitive systems.
- Enforce the Use of VPN for Remote Access: Clearly state in the policy that VPN use is mandatory for remote access to sensitive corporate systems. Whether employees are working from home or accessing systems outside the office network, the VPN should be used consistently.
- Specify VPN Configuration Requirements: Outline specific configuration requirements for using the VPN. This may include settings for encryption protocols, secure tunneling, and any other parameters necessary for a secure connection.
- Regularly Update VPN Software: Include a provision in the policy for regularly updating VPN software. This ensures that employees are using the latest security features and patches to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Monitor and Audit VPN Usage: Establish procedures for monitoring and auditing VPN usage. Regularly review logs and reports to ensure compliance with the policy. This helps identify any irregularities or potential security incidents.
- Conduct Periodic Security Awareness Training: Reinforce the importance of VPN use through periodic security awareness training. This can include reminders about the policy, updates on emerging threats, and best practices for maintaining a secure connection.
- Provide Support and Troubleshooting Assistance: Offer support resources and a help desk to assist employees with VPN-related issues. Ensure that staff members have access to troubleshooting guides and know where to seek assistance if they encounter problems.
- Establish Consequences for Non-Compliance: Clearly communicate the consequences of non-compliance with the VPN policy. This may include disciplinary actions or restrictions on accessing sensitive systems for employees who do not adhere to the policy.
- Regularly Review and Update the Policy: Periodically review and update the VPN policy to reflect changes in technology, security threats, or organizational needs. Ensure that the policy remains effective and aligned with industry best practices.
- Communicate Changes Effectively: Whenever there are updates or changes to the VPN policy, communicate these changes effectively to all staff members. Use various communication channels, such as email, intranet announcements, and team meetings.
- Obtain Employee Acknowledgment: Require employees to acknowledge and sign off on their understanding and acceptance of the VPN policy. This acknowledgement can be part of the on-boarding process for new hires and should be revisited periodically.
- Integrate with Remote Work Policies: If your organization supports remote work, integrate the VPN policy with remote work policies to ensure that employees maintain a secure connection when working outside the corporate network.
- Seek Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the VPN policy aligns with legal and regulatory requirements relevant to your industry. This is especially important for organizations that handle sensitive information subject to specific data protection laws.
- Encourage a Security-Conscious Culture: Foster a security-conscious culture within the organization. Encourage employees to prioritize security and understand their role in safeguarding sensitive information.
By implementing a well-defined VPN policy and fostering a culture of security awareness, your organization can significantly enhance its cybersecurity posture and protect sensitive corporate systems from potential threats.
Beware of logging on to corporate systems in public, using public WiFi, or near CCTV cameras!
Remote logging onto a corporate enterprise system introduces security challenges that require careful precautions to safeguard sensitive information and maintain the integrity of the organization’s digital assets. Here are key security precautions to take when remotely logging onto a corporate enterprise system:
- Use Secure Connections: Ensure that the connection to the corporate system is encrypted using secure protocols such as SSL/TLS. Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections provide an additional layer of encryption, securing data transmission between the remote device and the corporate network.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implement two-factor authentication for remote access. Require users to provide an additional authentication factor beyond the password, such as a temporary code sent to their mobile device. This enhances access security.
- Regularly Update Software and Systems: Keep remote devices, including laptops and mobile devices, up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This helps protect against known vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies for remote access accounts. Require complex passwords that include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Regularly prompt users to update their passwords.
- Secure Remote Desktop Protocols: If using remote desktop protocols, ensure that they are configured securely. Use strong encryption for remote desktop connections and avoid using default ports to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Limit Access Permissions: Implement the principle of least privilege by assigning access permissions based on job roles. Restrict remote users to only the resources and data necessary for their tasks, reducing the potential impact of a security breach.
- Beware of logging on to corporate systems in public or near CCTV cameras! In public places, it’s easy for someone to look over your shoulder and see sensitive information on your screen. Be aware of your surroundings and consider using a privacy screen on your laptop.
- Cameras in public places can capture your screen or keyboard, potentially exposing sensitive information. Be mindful of camera positions and try to position yourself in a way that minimizes exposure.
- Avoid using public computers for accessing corporate systems as they may be compromised with malware or key loggers.
- Keep your devices with you at all times. Unattended devices are easy targets for theft.
- Monitor and Audit Remote Access: Implement robust monitoring and auditing procedures for remote access. Regularly review logs for suspicious activities, unauthorized access attempts, or unusual patterns that may indicate a security threat.
- Endpoint Security: Ensure that remote devices have updated antivirus software and endpoint protection. Conduct regular security scans to detect and remove any malware or malicious software.
- Educate Users on Security Best Practices: Provide remote users with security awareness training. Educate them on phishing threats, social engineering tactics, and the importance of adhering to security policies when accessing corporate systems remotely.
- Secure WiFi Connections: If accessing corporate systems over WiFi, ensure that the connection is secure. Avoid using public or unsecured WiFi networks. Use WPA3 encryption for WiFi connections and consider using a VPN for an additional layer of security.
- Remote Device Management: Implement Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions for remote devices. This allows IT administrators to enforce security policies, track device locations, and remotely wipe devices in case of loss or theft.
PROTECTING SOFTWARE
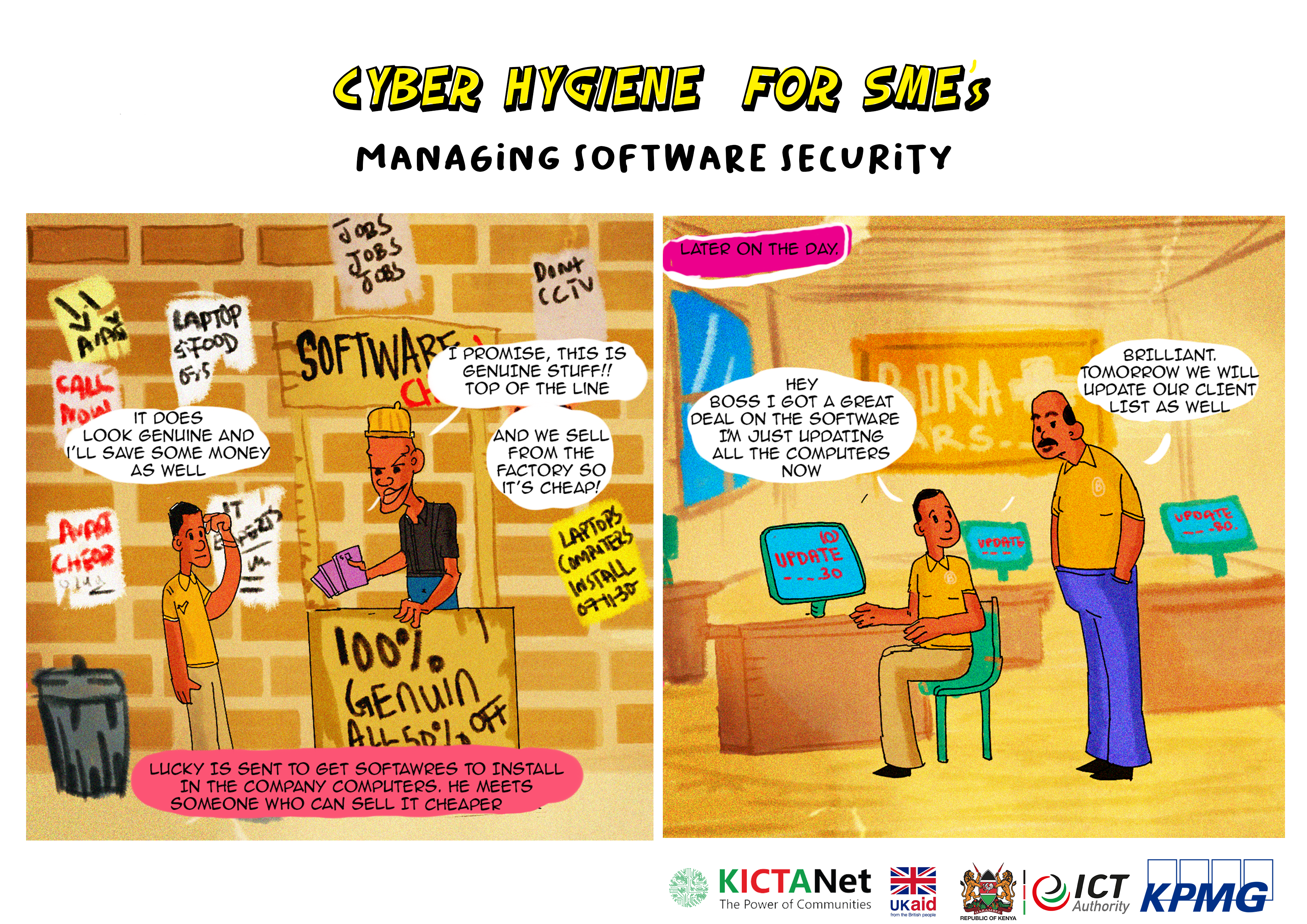
Be aware that a cracked or pirated version of software introduces weaknesses and risks to your corporation
Using cracked or pirated software poses significant cybersecurity risks, and it comes with various drawbacks compared to using legitimate versions of software. Here’s a contrast between the cybersecurity risks associated with cracked software and the benefits of using legitimate versions:
Cybersecurity Risks of Using Cracked Software:
1. Malware and Trojans: Cracked software often comes with modified or compromised executable files. These modifications can introduce malware, trojans, or other malicious code into the system, leading to unauthorized access and data breaches.
2. Vulnerability to Exploits: Cracked software may not receive security updates and patches from the official vendor. This leaves the software vulnerable to known exploits and vulnerabilities, increasing the risk of exploitation by cybercriminals.
3. Lack of Support and Updates: Users of cracked software typically miss out on official support and updates provided by legitimate vendors. In case of software issues or security vulnerabilities, there is no avenue for official assistance or fixes.
4. Compromised Corporate Information: Cracked software might be bundled with hidden functionalities that compromise user privacy. Personal information, such as login credentials, financial details, or browsing habits, can be at risk due to unauthorized access.
5. Legal Consequences: Using cracked software is illegal and can lead to legal consequences, including fines and potential lawsuits. Organizations distributing cracked software may also face legal action.
6. Incompatibility Issues: Cracked versions may lack proper activation or licensing mechanisms, leading to incompatibility issues with system updates or other software. This can result in system instability and performance issues.
7. Integrity Risks: The integrity of the cracked software itself is questionable. Users have no guarantee that the software has not been tampered with, leading to uncertainty regarding its behavior and reliability.
Benefits of Using Legitimate Software:
- Security Updates: Legitimate software vendors regularly release updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities and improve software functionality. Using genuine software ensures that you have access to these updates, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Official Support: Legitimate software comes with official support from the vendor. In case of issues or technical difficulties, users can seek assistance from the vendor’s support team, contributing to a smoother and more secure user experience.
- Compliance and Legal Security: Using legitimate software ensures compliance with licensing agreements and legal requirements. It eliminates the risk of legal consequences associated with piracy and provides a legal foundation for software usage.
- Reliability and Trustworthiness: Legitimate software is developed and distributed by trusted vendors. Users can have confidence in the integrity and reliability of the software, knowing that it has undergone quality assurance and meets industry standards.
- Reduced Malware Risks: Legitimate software obtained from official sources is less likely to be bundled with malware or malicious code. Vendors prioritize the security of their products and take measures to ensure the safety of users.
- Compatibility Assurance: Genuine software is designed to be compatible with other applications and system updates. This reduces the likelihood of incompatibility issues and ensures a seamless integration with the user’s environment.
- Access to Features and Functionality: Legitimate software provides access to the full range of features and functionalities intended by the vendor. Cracked versions may lack certain features or exhibit limitations that impact the user experience.
In summary, while using cracked or pirated software may seem like a cost-saving measure, it introduces substantial cybersecurity risks and legal consequences. Investing in legitimate software not only enhances security but also provides users with official support, regular updates, and a reliable and trustworthy computing environment.
Keep software updated and in line with the manufacturer’s recommendations
Outdated digital devices, including computers, smartphones, routers, and other connected devices, pose significant security risks for several reasons. As technology advances, manufacturers release updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities and improve the overall security posture of their devices. When devices become outdated and no longer receive updates, they are more susceptible to various security threats.
Here are some ways in which outdated digital devices can pose security risks:
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Manufacturers regularly release software updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities discovered in their devices. Outdated devices no longer receive these updates, leaving known vulnerabilities unpatched. Cyber criminals often exploit these vulnerabilities to compromise the security of devices.
- Increased Exposure to Malware: Outdated devices are more susceptible to malware attacks. Malicious actors develop new malware to exploit vulnerabilities, and outdated devices become easy targets. Malware can lead to various security issues, including data breaches, unauthorized access, and system instability.
- Lack of Security Features: Newer devices often come with enhanced security features to protect against evolving threats. Outdated devices may lack these advanced security features, making them more vulnerable to attacks that modern security measures could otherwise prevent.
- Incompatibility with Security Standards: Over time, security standards and protocols evolve to address emerging threats. Outdated devices may not support the latest security standards, leaving them unable to benefit from improved encryption methods and other security measures.
- Obsolete Encryption Algorithms: Older devices may use outdated or vulnerable encryption algorithms that are no longer considered secure. This makes it easier for attackers to intercept and decipher sensitive data transmitted by these devices.
- Limited or No Support: Manufacturers typically provide support, including security updates and technical assistance, for a limited time. Once a device reaches the end of its support life, it may no longer receive updates or assistance. This lack of support leaves users without recourse when facing security issues.
- Compromised User Data: Outdated devices are more likely to be targeted for data breaches. Cyber criminals exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to user data, including personal information, login credentials, and financial details.
- Weakened Network Security: Outdated routers and networking devices may have unpatched vulnerabilities that can be exploited to compromise the entire network. This can lead to unauthorized access to connected devices and potential data breaches.
- Increased Attack Surface: Keeping software updated is crucial for several reasons, primarily related to security, functionality, and performance. Here’s why it’s important to keep software up to date, along with an overview of how software is typically updated:
Importance of Keeping Software Updated:
- Security Patches: Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities discovered after the initial release. Regular updates help protect your system from exploitation by malicious actors seeking to take advantage of known weaknesses.
- Protection Against Exploits: Cyber criminals actively seek and exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Regular updates make it more difficult for attackers to target your system, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Bug Fixes: Updates often include bug fixes that address issues or errors in the software. Keeping your software current ensures a more stable and reliable user experience by resolving known problems.
- Performance Enhancements: Software updates may include optimizations and performance improvements, leading to a smoother and faster user experience. This can result in improved efficiency and responsiveness.
- Compatibility with New Technologies: As technology evolves, software updates ensure compatibility with new hardware, operating systems, and emerging technologies. Staying up to date allows you to leverage the latest features and advancements.
- Feature Enhancements: Software updates frequently introduce new features, capabilities, or improvements to existing functionalities. Keeping your software current ensures that you can benefit from the latest innovations.
- Vendor Support: Software vendors typically provide support for the latest versions of their products. Using outdated software may limit your access to official support, making it more challenging to resolve issues or seek assistance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Certain industries and organizations are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate the use of updated and secure software. Keeping software up to date helps ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
HOW SOFTWARE IS UPDATED
- Automatic Updates: Many software applications offer automatic update features. Users can configure the software to check for updates regularly and install them automatically. This ensures that security patches and improvements are applied without manual intervention.
- Manual Updates: Users can manually check for updates and initiate the update process. This is common for applications that do not have automatic update functionality or for users who prefer to control when updates are installed.
- Centralized Update Managers: Some operating systems or software suites have centralized update managers that facilitate the management of updates for multiple applications. Users can access a central dashboard to view and install updates for various software.
- Notification Systems: Software vendors often notify users about available updates through notifications within the application or via email. Users receive information about the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches, prompting them to update.
- Online Updates: Software updates can be delivered directly from the vendor’s servers to the user’s device over the internet. This online update process ensures that users receive the latest versions of the software.
- App Stores: Mobile and desktop platforms often have app stores where users can download and update applications. App stores provide a centralized location for managing updates for multiple applications.
- Version Control Systems: In the context of software development, version control systems are used to manage and update code repositories collaboratively. Developers can push updates to a central repository, and users can pull the latest version to their local environments.
- Patch Management Systems: Enterprise environments often use patch management systems to deploy updates across a large number of devices. These systems streamline the update process, ensuring that all devices in a network are consistently updated.
Keeping software updated involves a combination of automated and manual processes, depending on the software and the user’s preferences. Regardless of the method, staying informed about available updates and promptly applying them is essential for maintaining a secure and efficient computing environment.
Always procure software from reputable companies that can provide adequate customer support
Procuring software from a reputable dealer with adequate after-sales support is essential to ensure a smooth and reliable experience. Here are steps you can take to procure software from such a dealer:
- Research Reputable Dealers: Start by researching and identifying reputable dealers or authorized resellers of the specific software you need. Look for dealers with a proven track record, positive customer reviews, and recognition from the software vendor.
- Visit Official Vendor Websites: Visit the official website of the software vendor. Most vendors provide a list of authorized dealers or resellers on their website. Verify the authenticity of dealers by checking against the vendor’s official partner program or directory.
- Check Vendor Certifications: Look for certifications or partnerships between the dealer and the software vendor. Authorized dealers often have certifications that validate their status as legitimate and authorized distributors.
- Ask for Recommendations: Seek recommendations from colleagues, industry peers, or online communities that have experience with the software you’re interested in. Personal recommendations can provide valuable insights into the reliability of dealers.
- Contact the Software Vendor: Contact the software vendor directly and inquire about authorized dealers or resellers in your region. The vendor can provide information on trustworthy partners and guide you on how to verify their legitimacy.
- Check Business Reputation: Investigate the reputation of potential dealers by checking online reviews, testimonials, and ratings. Look for feedback from customers who have purchased software from the dealer, paying attention to their experiences with after-sales support.
- Inquire About After-Sales Support: Before making a purchase, inquire about the after-sales support provided by the dealer. Ask about customer service channels, response times, and the scope of support services. Reputable dealers prioritize customer satisfaction and provide comprehensive after-sales support.
- Verify Contact Information: Ensure that the dealer’s contact information, including phone numbers, email addresses, and physical address, is clearly provided on their website. Legitimate dealers are transparent about their contact details.
- Check for Authorized Channels: Ensure that the dealer is an authorized channel for the specific software you intend to purchase. Authorized dealers have direct access to software licenses, updates, and support from the vendor.
- Review Terms and Conditions: Thoroughly review the terms and conditions, including warranty information and return policies. Reputable dealers have clear and fair terms, and they stand by the quality of the products they sell.
- Compare Prices: While price is a consideration, be cautious of deals that seem too good to be true. Authorized dealers typically offer competitive but realistic pricing. Be wary of significantly discounted prices from unauthorized sources.
- Ask for References: Request references from the dealer, especially if you are making a substantial purchase. Contacting other customers can provide insights into their experiences with both the procurement process and after-sales support.
- Check for Red Flags: Be alert to red flags such as unclear pricing, unprofessional communication, or requests for payment through unconventional methods. These can indicate potential scams or unauthorized dealers.
- Clarify Licensing and Terms: Clearly understand the licensing terms and conditions associated with the software. Authorized dealers provide legitimate licenses and ensure compliance with the vendor’s licensing agreements.
- Keep Records: Keep detailed records of your communication with the dealer, including quotes, invoices, and any commitments regarding after-sales support. This documentation can be valuable in case of disputes or issues.
By taking these steps, you can increase the likelihood of procuring software from a reputable dealer with adequate after-sales support. Prioritizing the legitimacy of the dealer ensures that you receive genuine software, benefit from proper support, and avoid potential risks associated with unauthorized sources.
STAYING SAFE ON SOCIAL MEDIA
Factors to consider when choosing the right social media platform to reach your audience
Choosing the right social media platforms for a small business is crucial for effective brand promotion and product marketing. Different platforms cater to diverse audiences and content types, so it’s essential to consider various factors when making this decision. Here are key factors to take into account when selecting social media platforms for business promotion:
- Target Audience: Identify your target audience and their preferred social media platforms. Consider demographics such as age, location, interests, and behavior. Choose platforms where your potential customers are most active.
- Business Goals and Objectives: Define your business goals and marketing objectives. Different social media platforms excel at various objectives, such as brand awareness, lead generation, engagement, or sales. Align your goals with the platform’s strengths.
- Content Type and Format: Assess the types of content you plan to create. Different platforms support different content formats, including images, videos, text-based posts, stories, and live broadcasts. Choose platforms that align with your content strategy.
- Industry and Niche: Consider the industry or niche your business operates in. Certain platforms may be more popular or effective for specific industries. Research industry leaders to see which platforms they leverage.
- Time and Resource Constraints: Consider the time and resources you can allocate to social media marketing. Managing multiple platforms can be time-consuming. Start with a manageable number and expand as your capacity grows.
- Engagement and Interaction: Assess the level of engagement and interaction on each platform. Some platforms encourage more direct engagement and conversations, while others are more suited for broadcasting content. Choose platforms that align with your desired level of interaction.
- Analytics and Insights: Consider the analytics and insights tools provided by each platform. Access to data on audience demographics, post performance, and engagement metrics can inform your strategy. Choose platforms that offer valuable analytics.
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations: Be aware of legal and regulatory considerations related to your industry and target markets. Some industries have specific guidelines or restrictions on certain types of content or advertising.
- Integration with Other Tools: Consider how well the chosen platforms integrate with other tools and technologies your business uses. Seamless integration can streamline workflows and improve efficiency.
- Community Building Opportunities: Some platforms offer strong community-building features, such as groups or forums. If community engagement is a priority, choose platforms that facilitate the creation and growth of communities.
Activate and configure the security features built within the social media platforms
Considering the security features of social media platforms is essential for protecting corporate information, maintaining privacy, complying with legal standards, and safeguarding overall well-being in the digital space. Some of these security features include:
- Account Authentication and Authorization: Features like two-factor authentication (2FA) add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification beyond just a password. This helps prevent unauthorized access to accounts.
- Privacy Settings: Social media platforms offer privacy settings that allow users to control who can see their posts, profile information, and friend lists. Understanding and configuring these settings is essential for managing one’s online presence.
- Activity Monitoring and Alerts: Some platforms provide features that allow users to monitor and receive alerts about suspicious activity on their accounts. This can help users detect unauthorized access or potential security threats.
- Secure Connection (HTTPS): Social media platforms often use secure connections (HTTPS) to encrypt data transmitted between the user’s device and the platform’s servers, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept or tamper with the communication.
- Account Recovery Options: In the event of a forgotten password or a compromised account, platforms usually provide account recovery options. These features should be set up correctly to ensure a secure and reliable recovery process.
- Blocking and Reporting Features: Social media apps include tools to block or report users engaging in harmful behavior. These features contribute to creating a safer online environment by allowing users to control their interactions.
- Location and Tagging Controls: Many social media platforms allow users to control the visibility of their location and tagging in posts. Managing these settings is important for maintaining personal security and privacy.
- Reviewing Connected Apps and Permissions: Social media platforms often integrate with third-party apps. Users should periodically review and manage the apps connected to their accounts, ensuring that they only grant necessary permissions and revoke access to unused apps.
- Incident Response and Support: Platforms with robust security features often have mechanisms in place for users to report security incidents or seek support in case of account compromise. Knowing how to use these resources can be vital in recovering from security incidents.
- Regular Updates: Social media apps frequently release updates that may include security patches. Keeping the app updated ensures that users benefit from the latest security enhancements and bug fixes.
Monitor your social media platforms for suspicious activity
The frequency of monitoring social media platforms for a small business depends on various factors, including the level of activity, the size of the audience, the industry, and the business goals. Here are general guidelines for monitoring social media platforms:
- Real-Time Monitoring for Critical Issues: It is crucial to have real-time monitoring for critical issues, such as customer complaints, emerging crises, or urgent inquiries. Set up notifications to be alerted immediately to such matters.
- Daily Monitoring:
- Response to Direct Messages and Comments: Small businesses should aim to check direct messages and comments daily. Responding promptly to customer inquiries, comments, or mentions demonstrates attentiveness and fosters positive interactions.
- Monitoring Mentions and Tags: Keep track of brand mentions and tags. This includes mentions in posts, stories, and comments. Monitoring mentions helps you stay aware of how your brand is being discussed and allows you to engage with user-generated content.
- Checking Analytics and Performance Metrics: Review key performance metrics daily, especially if you are running active campaigns. This includes tracking engagement, reach, and other relevant analytics to assess the performance of your content.
- Weekly Monitoring:
- Content Performance Review: Conduct a weekly review of the performance of your content. Evaluate which posts gained the most engagement, what type of content resonated with your audience, and adjust your content strategy accordingly.
- Responding to Reviews: If your business receives online reviews, monitor and respond to them weekly. Positive reviews can be acknowledged, while any negative feedback should be addressed promptly and professionally.
- Checking for Trends and Industry News: Stay informed about trends and industry news by monitoring relevant hashtags or keywords. This can help you participate in conversations, share timely content, and position your business as knowledgeable in your industry.
- Monthly Monitoring:
- Overall Performance Analysis: Conduct a monthly analysis of your social media performance. Evaluate your overall social media strategy, assess the growth of your audience, and identify areas for improvement.
- Competitor Analysis: Monitor the social media activities of competitors on a monthly basis. Analyze their content, engagement strategies, and audience interactions. Identify opportunities to differentiate your approach and stay competitive.
- Reviewing Goals and Objectives: Revisit your social media goals and objectives to ensure alignment with broader business goals. Assess whether your current strategy is helping you achieve these objectives and make adjustments as needed.
- Quarterly Monitoring:
- Strategy Assessment and Adjustment: Conduct a comprehensive review of your social media strategy on a quarterly basis. Assess the effectiveness of your campaigns, review the performance of different content types, and adjust your strategy based on insights gained.
- Audit and Cleanup: Perform a quarterly audit of your social media accounts. This includes reviewing your follower list, updating profile information, and ensuring that all content aligns with your current brand messaging.
- Identifying Emerging Trends: Look for emerging trends or changes in user behavior. Stay adaptable by incorporating new features or adjusting your strategy to capitalize on evolving trends in social media.
SECURING DEVICES
Avoid using outdated devices for processing or storage
Outdated digital devices, including computers, smartphones, routers, and other connected devices, pose significant security risks for several reasons. As technology advances, manufacturers release updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities and improve the overall security posture of their devices. When devices become outdated and no longer receive updates, they are more susceptible to various security threats.
Here are some ways in which outdated digital devices can pose security risks:
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Manufacturers regularly release software updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities discovered in their devices. Outdated devices no longer receive these updates, leaving known vulnerabilities unpatched. Cyber criminals often exploit these vulnerabilities to compromise the security of devices.
- Increased Exposure to Malware: Outdated devices are more susceptible to malware attacks. Malicious actors develop new malware to exploit vulnerabilities, and outdated devices become easy targets. Malware can lead to various security issues, including data breaches, unauthorized access, and system instability.
- Lack of Security Features: Newer devices often come with enhanced security features to protect against evolving threats. Outdated devices may lack these advanced security features, making them more vulnerable to attacks that modern security measures could otherwise prevent.
- Incompatibility with Security Standards: Over time, security standards and protocols evolve to address emerging threats. Outdated devices may not support the latest security standards, leaving them unable to benefit from improved encryption methods and other security measures.
- Obsolete Encryption Algorithms: Older devices may use outdated or vulnerable encryption algorithms that are no longer considered secure. This makes it easier for attackers to intercept and decipher sensitive data transmitted by these devices.
- Limited or No Support: Manufacturers typically provide support, including security updates and technical assistance, for a limited time. Once a device reaches the end of its support life, it may no longer receive updates or assistance. This lack of support leaves users without recourse when facing security issues.
- Compromised User Data: Outdated devices are more likely to be targeted for data breaches. Cyber criminals exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to user data, including personal information, login credentials, and financial details.
- Weakened Network Security: Outdated routers and networking devices may have unpatched vulnerabilities that can be exploited to compromise the entire network. This can lead to unauthorized access to connected devices and potential data breaches.
- Increased Attack Surface: Outdated devices contribute to an organization’s or individual’s overall attack surface. A larger attack surface provides more opportunities for cyber criminals to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Elevated Risk in IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as smart home devices and industrial sensors, often have limited resources and may not receive regular updates. Outdated IoT devices can become entry points for attackers to infiltrate networks and compromise connected systems.
- Regulatory Compliance Concerns: In some industries, regulatory compliance requires the use of secure and up-to-date technology. Using outdated devices may lead to non-compliance with industry regulations, potentially resulting in legal and financial consequences.
To mitigate these security risks, users and organizations should regularly update their digital devices, retire outdated hardware when necessary, and follow best practices for securing their network and systems. Regular software updates, implementing security protocols, and staying informed about potential vulnerabilities are essential measures to maintain a secure digital environment.
Physically secure devices such as a laptop and servers by keeping them in a lockable and secure area
Certain types of digital technology and equipment should ideally be kept in a locked room or secure area to enhance physical security and prevent unauthorized access. The decision to secure these devices depends on the sensitivity of the data they contain and the potential impact of their compromise. Here are examples of digital technology that might be kept in a locked room or secure environment:
- Servers and Data Centers: Critical servers and data center equipment that store sensitive and essential data should be kept in a secured room. This prevents unauthorized physical access and helps protect against theft, tampering, or damage.
- Network Infrastructure: Networking equipment, including routers, switches, and firewalls, should be kept in a secure area. Unauthorized access to these devices could potentially compromise network security and lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Backup Systems: Backup servers and systems containing backup copies of critical data should be stored securely. Backups often contain sensitive information and are crucial for disaster recovery. Securing them helps prevent data loss and unauthorized access.
- Sensitive Data Storage Devices: Devices that store sensitive data, such as external hard drives, USB drives, or other removable media, should be kept in a secure location. This prevents data leakage and reduces the risk of unauthorized copying or removal.
- Security Monitoring Equipment: Devices used for security monitoring, such as surveillance cameras, DVRs (Digital Video Recorders), and monitoring servers, should be placed in a locked room. This protects the integrity of the monitoring system and prevents tampering.
- Access Control Systems: Physical access control systems, including card readers, biometric scanners, and related infrastructure, should be secured to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive areas of a facility.
- Encryption Key Storage: Devices or hardware security modules (HSMs) used for storing encryption keys and ensuring the security of cryptographic operations should be kept in a highly secure environment to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive keys.
- Sensitive Testing and Development Environments: Testing and development environments that replicate production systems with sensitive data should be secured. This prevents unauthorized access to pre-production systems and protects sensitive test data.
- Industrial Control Systems (ICS): Equipment used in industrial control systems, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, should be physically secured to prevent unauthorized interference with critical infrastructure.
- Biometric Access Devices: Biometric authentication devices, such as fingerprint scanners or retina scanners, should be secured to prevent tampering or unauthorized access attempts.
- Sensitive Hardware Components: High-value or critical hardware components, such as specialized processors, cryptographic hardware, or hardware security modules, should be stored securely to prevent theft or tampering.
- Telecommunications Equipment: Infrastructure related to telecommunications, including PBX (Private Branch Exchange) systems and communication servers, should be kept secure to prevent unauthorized access and eavesdropping.
- Medical Equipment with Patient Data: Medical devices that store patient data, such as electronic health records (EHRs) or medical imaging systems, should be secured to protect patient privacy and comply with healthcare regulations.
- Financial Systems: Devices handling financial transactions or containing sensitive financial information, such as ATMs, point-of-sale systems, and banking servers, should be stored securely to prevent fraud and unauthorized access.
- Restricted Access Workstations: Workstations used for handling classified or sensitive information, especially in government, military, or research settings, should be located in secured rooms with controlled access.
When determining which digital technology should be kept in a locked room or secure environment, organizations should conduct a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. The level of security should align with the criticality of the systems and the sensitivity of the data they handle. Additionally, adherence to industry regulations and compliance standards may dictate specific security measures for certain types of technology.
Protect your devices with strong passwords and antivirus
Enabling a login password and installing antivirus software on digital devices are fundamental security practices that play a crucial role in safeguarding both personal and organizational information. These measures provide basic protection against a range of threats and help mitigate the risks associated with various cybersecurity issues. Here’s why it’s important to implement these security measures:
- Unauthorized Access Prevention: Login Password: A login password serves as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to a device. It helps prevent individuals who do not have the correct credentials from gaining access to personal or sensitive information.
- Data Confidentiality: Login Password: Password protection ensures the confidentiality of data on the device. Without the correct password, unauthorized users cannot access files, documents, or personal information stored on the device.
- Identity Protection: Login Password: A login password is essential for protecting user identities. It ensures that only authorized individuals can use the device and access associated accounts, reducing the risk of identity theft.
- Securing Personal and Financial Information: Login Password: Devices often store personal and financial information. A login password adds a layer of security, preventing unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data such as bank accounts, emails, and personal documents.
- Preventing Unauthorized Transactions: Login Password: For devices used for online banking or financial transactions, a login password is crucial to prevent unauthorized individuals from making transactions on behalf of the device owner.
- Protection Against Physical Theft: Login Password: In the event of device theft, a login password helps protect the data on the device. Without the correct password, thieves may find it challenging to access and misuse the information.
- Malware and Cyber Threat Prevention: Antivirus Software: Antivirus software detects and removes malware, including viruses, trojans, and ransomware. It provides real-time protection against malicious software that could compromise the device’s security.
- Email Security: Antivirus Software: Antivirus solutions often include email scanning capabilities, helping to identify and block malicious attachments or links in emails. This is critical for preventing phishing attacks and email-borne malware.
- Web Browsing Protection: Antivirus Software: Many antivirus programs offer web protection features that help users avoid malicious websites. This is especially important for preventing drive-by downloads and other web-based threats.
- Protection Against Exploits: Antivirus Software: Antivirus programs are designed to detect and prevent the exploitation of software vulnerabilities. They help safeguard against threats that exploit weaknesses in operating systems and applications.
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Antivirus Software: Antivirus solutions often provide regular updates to their virus definitions and security databases. This ensures that the software is equipped to identify and respond to the latest threats.
- Behavioral Analysis: Antivirus Software: Advanced antivirus solutions employ behavioral analysis to identify suspicious activities or patterns that may indicate the presence of malware. This proactive approach enhances detection capabilities.
- File and System Integrity: Antivirus Software: Antivirus programs monitor files and system activities for signs of compromise. They help maintain the integrity of the device by detecting and quarantining malicious files.
- Protection Across Multiple Devices: Antivirus Software: Many antivirus solutions offer multi-device protection, allowing users to secure not only their computers but also smartphones and tablets. This comprehensive coverage helps maintain a consistent security posture.
- Compliance with Best Practices: Login Password and Antivirus Software: Enabling a login password and installing antivirus software align with cybersecurity best practices.
SETTING UP A PASSWORD OR PIN
- Open Settings: Unlock your Android device and navigate to the “Settings” app. The icon may look like a gear or a set of sliders, depending on your device and Android version.
- Go to Security or Biometrics and Security: Scroll down or look for the “Security” option in the Settings menu. On some devices, you may find it under “Biometrics and Security” or a similar category.
- Choose Screen Lock or Lock Screen: Look for an option like “Screen Lock” or “Lock Screen” within the Security settings. Tap on it to proceed.
- Select Password or PIN: You’ll likely see options such as “None,” “Swipe,” “Pattern,” “PIN,” or “Password.” Choose either “Password” or “PIN” based on your preference.
- Set Up the Password or PIN: Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your password or PIN. For a password, enter a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. For a PIN, choose a numeric code.
- Confirm the Password or PIN: You’ll be prompted to enter the password or PIN again to confirm. This ensures that you haven’t made any mistakes during the setup process.
- Additional Security Settings (Optional): Some devices may offer additional security settings, such as enabling Smart Lock, which allows the device to remain unlocked in certain trusted situations (e.g., when connected to a specific Bluetooth device).
- Done: Once you’ve completed the setup, your Android device will now require the password or PIN to unlock the screen.
SETTING UP A PATTERN
If you prefer a pattern over a password or PIN:
- Follow Steps 1-3 Above: Open Settings, go to Security or Biometrics and Security, and choose Screen Lock or Lock Screen.
- Select Pattern: Choose the “Pattern” option from the available screen lock methods.
- Draw Your Pattern: Follow the on-screen instructions to draw a pattern by connecting at least four dots. Ensure it’s something memorable and unique to you.
- Confirm the Pattern: Draw the same pattern again to confirm your choice.
- Additional Security Settings (Optional): Similar to the password or PIN setup, you may have additional security settings to configure.
- Done: Your Android device will now require the drawn pattern to unlock the screen.
Once you’ve set up the password, PIN, or pattern, your Android device is secured with a login password, providing an additional layer of protection for your data and privacy. Always ensure that you remember the chosen password, PIN, or pattern to avoid being locked out of your device.
CHOOSING A QUALITY ANTIVIRUS
Choosing and installing a quality antivirus on your device is a crucial step in maintaining a secure digital environment. Here are guidelines to help you wisely choose and install a reliable antivirus solution:
- Research Reputable Brands: Start by researching well-known and reputable antivirus brands. Look for companies with a history of providing effective and reliable security solutions.
- Read Reviews and Recommendations: Read reviews and recommendations from reliable sources, including tech websites, user reviews, and independent testing organizations (such as AV-TEST and AV-Comparatives). Pay attention to how well the antivirus performs in real-world scenarios.
- Consider Features and Protection Levels: Evaluate the features offered by different antivirus solutions. Look for features such as real-time scanning, phishing protection, firewall, behavior analysis, and automatic updates. Ensure the chosen antivirus provides comprehensive protection against a range of threats.
- Compatibility with Your Device: Check whether the antivirus solution is compatible with your specific device and operating system (e.g., Windows, MacOS, Android). Some antivirus programs are designed for specific platforms, so choose one that suits your device.
- Resource Usage: Consider the impact of the antivirus on your device’s performance. Choose an antivirus solution that offers effective protection without significantly slowing down your system.
- Ease of Use: Opt for an antivirus with a user-friendly interface and straightforward settings. A solution that is easy to use ensures that you can navigate through settings, perform scans, and manage security features without complications.
- Customer Support: Check the availability and quality of customer support provided by the antivirus vendor. This is important in case you encounter issues or have questions about the product.
- Cost and Licensing: Consider the cost and licensing options. Some antivirus solutions offer free versions with basic protection, while premium versions provide advanced features. Ensure that the chosen antivirus fits your budget and meets your security needs.
- Frequency of Updates: Regular updates are crucial for keeping the antivirus software effective against emerging threats. Choose a solution that provides frequent and automatic updates to its virus definitions and security databases.
- Independent Test Results: Look for antivirus solutions that have been independently tested by reputable organizations. Independent testing labs assess the effectiveness of antivirus programs in detecting and blocking various types of malware.
INSTALLING AN ANTIVIRUS
- Download from Official Sources: Always download the antivirus software from the official website of the vendor or from trusted app stores. Avoid downloading from third-party sources to reduce the risk of downloading compromised or fake software.
- Follow Installation Instructions: Carefully follow the installation instructions provided by the antivirus vendor. Pay attention to any specific settings or configurations recommended during the installation process.
- Configure Settings: Once installed, configure the antivirus settings according to your preferences. This may include setting up scheduled scans, adjusting real-time protection settings, and enabling additional security features.
- Perform Initial Scan: Run a full system scan immediately after installation to check for any existing threats on your device. This helps ensure that your device is free from malware from the outset.
- Enable Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates to ensure that your antivirus stays up to date with the latest threat definitions and security patches. Regular updates are critical for maintaining the effectiveness of the antivirus.
- Schedule Regular Scans: Schedule regular scans of your device to proactively detect and remove any potential threats. This helps prevent malware from persisting on your system undetected.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the security status of your device through the antivirus interface. Pay attention to any notifications or alerts provided by the antivirus regarding potential threats or security issues.
- Update Other Software: Keep other software and applications on your device updated, as vulnerabilities in non-antivirus software can be exploited by malware. Regularly check for updates to your operating system and other applications.
- Monitor and Renew Subscriptions: If you’re using a paid antivirus solution with a subscription, monitor the expiration date and renew the subscription on time to ensure continuous protection.
By carefully choosing a reputable antivirus solution and following proper installation and configuration practices, you can enhance the security of your device and protect against a wide range of cyber threats. Regularly update the antivirus software, stay vigilant for security alerts, and practice safe online behavior to maintain a secure digital environment.
Switch off device camera and microphone when not in use
Switching off and covering a device’s camera and microphone when not in use is a security measure that helps protect user privacy and guard against potential risks. Here are reasons why it is wise to take these precautions:
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: Covering the camera ensures that even if a device is compromised, an attacker cannot gain unauthorized access to the camera feed. Malicious software or remote exploits could potentially activate the camera without the user’s knowledge.
- Mitigating Privacy Concerns: Covering the camera is a simple yet effective way to address privacy concerns. It prevents accidental or intentional recording of users in their private spaces, protecting individuals from unwarranted surveillance.
- Avoiding Webcam Hacking: Webcam hacking is a type of cyber threat where attackers gain control of a device’s camera. By covering the camera when it’s not in use, users can thwart attempts to compromise their privacy through unauthorized webcam access.
- Protecting Against Spying Malware: Certain types of malware, such as remote access trojans (RATs), are designed to take control of a device’s camera and microphone. Covering these components prevents the malware from capturing audio or video without the user’s consent.
- Preventing Visual Eavesdropping: Uncovered cameras can inadvertently capture sensitive or private moments. Covering the camera provides an extra layer of assurance against accidental visual eavesdropping, especially in environments where privacy is crucial.
- Securing Confidential Conversations: Covering the microphone when not in use ensures that confidential conversations are not inadvertently recorded. This precaution is particularly relevant for devices with voice-activated features that may inadvertently capture conversations.
- Avoiding Physical Surveillance: In situations where devices are left unattended or in shared spaces, covering the camera prevents physical surveillance. It mitigates the risk of someone intentionally or unintentionally activating the camera to monitor activities.
- Preventing Remote Hijacking: In some cases, attackers may attempt to remotely hijack a device’s camera or microphone. Covering these components reduces the risk of such attacks, even if the device is compromised or targeted.
- Building Trust with IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices with cameras and microphones can introduce privacy concerns. Covering these components when not in use helps build trust with users, assuring them that their privacy is a priority.
- Protecting Against Deepfake Threats: Deepfake technology uses manipulated audio and video to create realistic simulations of individuals. By covering the camera and microphone, users reduce the risk of unauthorized recordings that could be used in deep fake content.
- Demonstrating Physical Security Awareness: Covering the camera and microphone sends a visual signal that the user is conscious of security and privacy risks. It serves as a practical and proactive step in protecting personal information.
- Compliance with Security Best Practices: Security best practices often recommend covering cameras and disabling microphones when not in use. Adhering to these recommendations aligns with proactive cybersecurity measures.
- Preventing Unintentional Activation: Some devices, especially those with voice-activated assistants, may unintentionally activate the microphone. Covering the microphone prevents unintentional recording of conversations or ambient sounds.
- Personal Control Over Privacy: Covering the camera and microphone gives users a sense of control over their privacy. It allows individuals to decide when these components are active and when they are not, reducing reliance on default settings.
While these measures can enhance privacy and security, it’s also important to keep software and firmware up to date, use reputable security software, and be cautious about granting unnecessary permissions to applications. Cybersecurity is a multi-layered approach, and covering the camera and microphone is just one part of maintaining a secure digital environment.
Use a privacy screen on your devices to protect your data from prying eyes
A privacy screen, also known as a privacy filter or screen protector, is a physical overlay that can be attached to the display of a digital device, such as a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. The primary purpose of a privacy screen is to limit the viewing angles of the screen, making it more difficult for people around you to see the content displayed on your device. This technology is especially useful in maintaining privacy and preventing unauthorized individuals from viewing sensitive information.
WHY A PRIVACY SCREEN IS USEFUL:
- Confidentiality Protection: A privacy screen helps protect confidential and sensitive information by narrowing the viewing angle. This is particularly valuable when working on sensitive documents, financial information, or personal content in public spaces.
- Preventing Shoulder Surfing: Shoulder surfing refers to the practice of someone looking over your shoulder to see what you’re doing on your device. A privacy screen minimizes the risk of shoulder surfing by obscuring the content from prying eyes.
- Enhancing Data Security: In environments where data security is critical, such as in corporate settings or while traveling, a privacy screen adds an extra layer of defense against unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Maintaining Professional Privacy: Professionals working on confidential projects or dealing with sensitive client information can use privacy screens to maintain the privacy of their work in shared workspaces or during business trips.
- Preserving Personal Privacy: For personal devices, a privacy screen ensures that your private communications, messages, or browsing activities are not inadvertently exposed to people nearby.
HOW TO CHOOSE A PRIVACY SCREEN
- Compatibility: Ensure that the privacy screen is compatible with the size and aspect ratio of your device’s display. Measure your device’s screen dimensions or check the manufacturer’s specifications to find a suitable privacy screen.
- Viewing Angle: Consider the viewing angle of the privacy screen. Choose one that provides an optimal balance between privacy and usability. Some privacy screens are designed to be effective only when viewed straight on, while others offer a wider range of angles.
- Anti-Glare Properties: Look for privacy screens with anti-glare properties. This feature not only enhances privacy but also reduces reflections and glare, improving visibility in various lighting conditions.
- Easy Installation: Choose a privacy screen that is easy to install and remove. Some screens use adhesive or attach with magnetic strips, while others may use a frame or clip-on design. Consider your preferences and the convenience of installation.
- Touchscreen Compatibility: If your device has a touchscreen, ensure that the privacy screen does not interfere with touch functionality. High-quality privacy screens are designed to maintain touchscreen responsiveness.
- Material and Build Quality: Consider the material and build quality of the privacy screen. High-quality materials enhance durability, scratch resistance, and overall performance. Some screens are also designed to protect the device’s display from scratches.
- Reversibility: Some privacy screens are reversible, allowing you to choose between a privacy side and a standard screen side. This flexibility can be beneficial in situations where privacy is not a concern.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Check whether the privacy screen is easy to clean and maintain. Smudge-resistant and fingerprint-resistant coatings can help keep the screen clear and provide a better viewing experience.
- Anti-Blue Light Features: Some privacy screens come with anti-blue light features, which can be beneficial for reducing eye strain and minimizing exposure to harmful blue light emitted by digital screens.
- Brand Reputation: Consider purchasing from reputable brands known for producing quality privacy screens. Read reviews and testimonials to gauge the experiences of other users with a particular privacy screen model.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the privacy screen complies with relevant regulations and standards. This is particularly important in professional settings where privacy measures may be subject to compliance requirements.
- Customization Options: Some privacy screens offer customizable features, such as adjustable viewing angles or the ability to switch between privacy mode and a standard display. Explore options that align with your preferences.
By carefully selecting a privacy screen that meets your device’s specifications and aligns with your privacy requirements, you can enhance the security of your digital activities and protect sensitive information from prying eyes in various environments.
SAFE ADOPTION OF EMERGING TECHNOLOGY
Adopt technologies that sustainably widen your market reach
Evaluating emerging technologies for their suitability in your small business involves a thoughtful and systematic approach. Here are steps you can take to assess whether a technology is a good fit for your business:
- Define Your Business Needs and Goals: Start by clearly defining your business needs, goals, and challenges. Understanding your specific requirements will help you identify technologies that address your pain points and align with your objectives.
- Research and Stay Informed: Stay informed about emerging technologies relevant to your industry. Regularly read industry publications, attend conferences, and follow reputable tech blogs to understand the latest advancements and trends.
- Assess Impact on Operations: Evaluate how the emerging technology will impact your business operations. Consider factors such as efficiency gains, cost savings, improved productivity, and enhanced customer experiences.
- Budget Considerations: Assess the cost implications of adopting the technology. Consider not only the initial investment but also ongoing costs, such as maintenance, upgrades, and potential training expenses. Ensure that the technology fits within your budget constraints.
- Compatibility with Existing Systems: Evaluate the compatibility of the emerging technology with your existing systems and infrastructure. A seamless integration with your current technology stack is essential to avoid operational challenges.
- Security and Compliance: Prioritize the security features of the technology. Assess its ability to safeguard sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry regulations and data protection standards relevant to your business.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the reputation of the technology vendor. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from other businesses that have implemented the technology. A reputable vendor is more likely to provide reliable products and support.
Gallery
Sponsors
![]()